Event-based sampled ECG morphology reconstruction through self-similarity
Paper and Code
Jul 05, 2022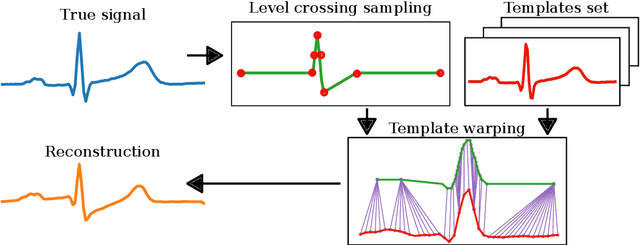

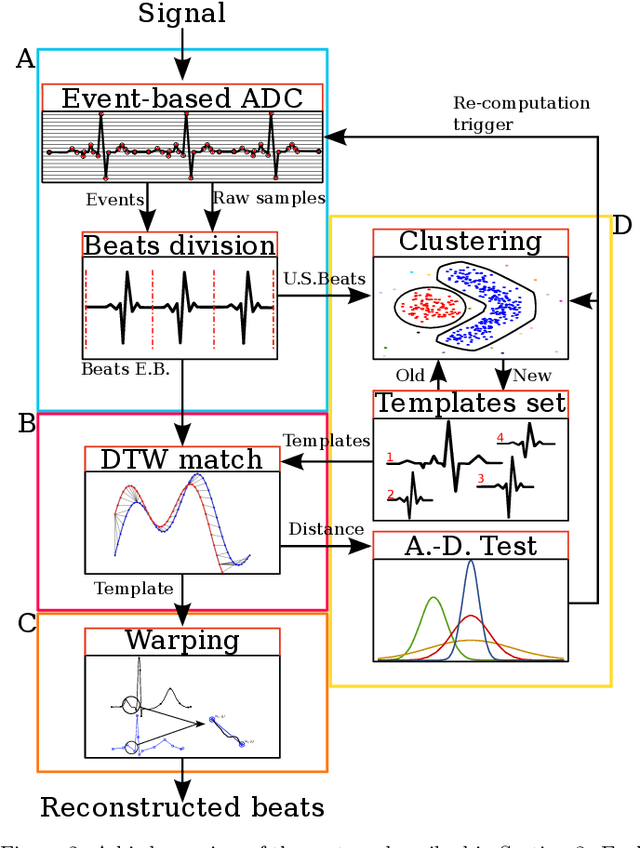

Background and Objective: Event-based analog-to-digital converters allow for sparse bio-signal acquisition, enabling local sub-Nyquist sampling frequency. However, aggressive event selection can cause the loss of important bio-markers, not recoverable with standard interpolation techniques. In this work, we leverage the self-similarity of the electrocardiogram (ECG) signal to recover missing features in event-based sampled ECG signals, dynamically selecting patient-representative templates together with a novel dynamic time warping algorithm to infer the morphology of event-based sampled heartbeats. Methods: We acquire a set of uniformly sampled heartbeats and use a graph-based clustering algorithm to define representative templates for the patient. Then, for each event-based sampled heartbeat, we select the morphologically nearest template, and we then reconstruct the heartbeat with piece-wise linear deformations of the selected template, according to a novel dynamic time warping algorithm that matches events to template segments. Results: Synthetic tests on a standard normal sinus rhythm dataset, composed of approximately 1.8 million normal heartbeats, show a big leap in performance with respect to standard resampling techniques. In particular (when compared to classic linear resampling), we show an improvement in P-wave detection of up to 10 times, an improvement in T-wave detection of up to three times, and a 30\% improvement in the dynamic time warping morphological distance. Conclusion: In this work, we have developed an event-based processing pipeline that leverages signal self-similarity to reconstruct event-based sampled ECG signals. Synthetic tests show clear advantages over classical resampling techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge