Evaluating Nonlinear Decision Trees for Binary Classification Tasks with Other Existing Methods
Paper and Code
Aug 25, 2020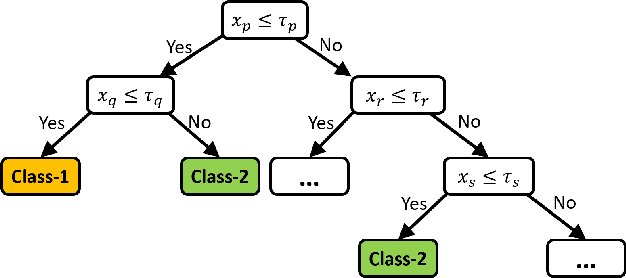
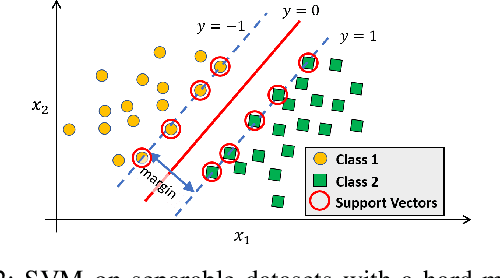
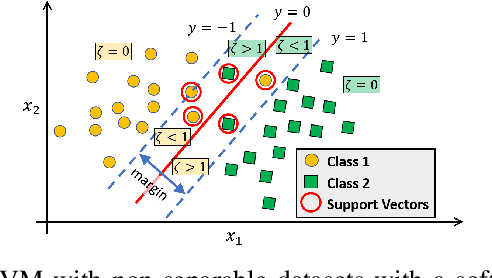
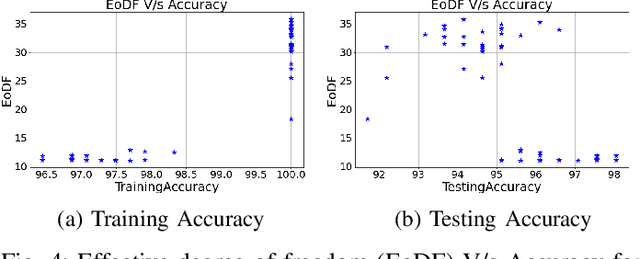
Classification of datasets into two or more distinct classes is an important machine learning task. Many methods are able to classify binary classification tasks with a very high accuracy on test data, but cannot provide any easily interpretable explanation for users to have a deeper understanding of reasons for the split of data into two classes. In this paper, we highlight and evaluate a recently proposed nonlinear decision tree approach with a number of commonly used classification methods on a number of datasets involving a few to a large number of features. The study reveals key issues such as effect of classification on the method's parameter values, complexity of the classifier versus achieved accuracy, and interpretability of resulting classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge