Evaluating Multi-Sensor Placement and Neural Network Architectures for Physical Activity Level Classification
Paper and Code
Feb 20, 2025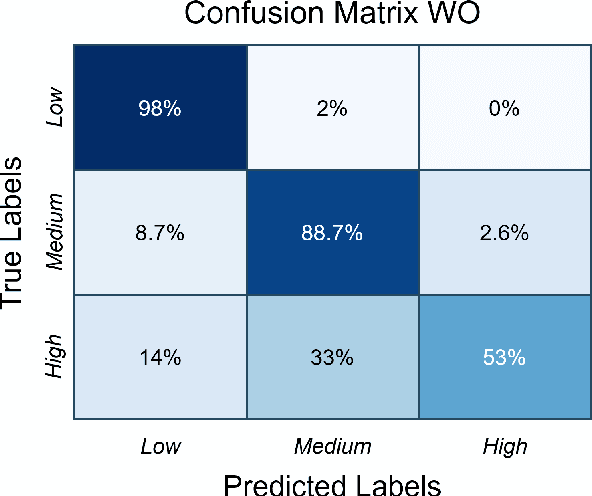
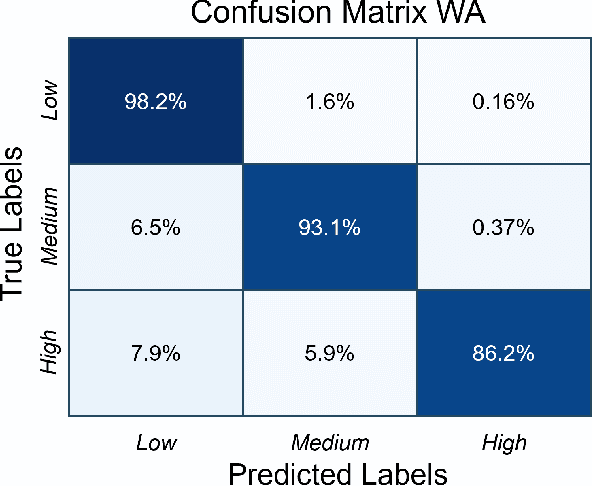
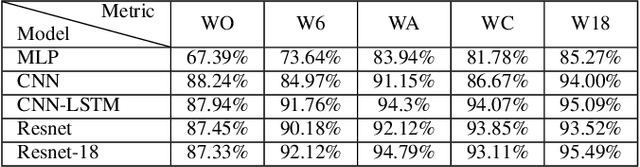
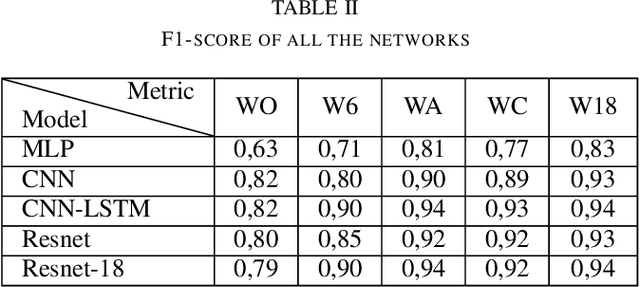
Accurate physical activity level (PAL) classification could be beneficial for osteoarthritis (OA) management. This study examines the impact of sensor placement and deep learning models on AL classification using the Metabolic Equivalent of Task values. The results show that the addition of anankle sensor (WA) significantly improves the classification of intensity activities compared to wrist-only configuration(53% to 86.2%). The CNN-LSTM model achieves the highest accuracy (95.09%). Statistical analysis confirms multi-sensor setups outperform single-sensor configurations (p < 0.05). The WA configuration offers a balance between usability and accuracy, making it a cost-effective solution for AL monitoring, particularly in OA management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge