Evaluating Driver Readiness in Conditionally Automated Vehicles from Eye-Tracking Data and Head Pose
Paper and Code
Jan 20, 2024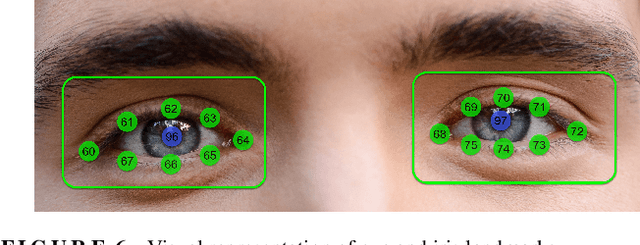
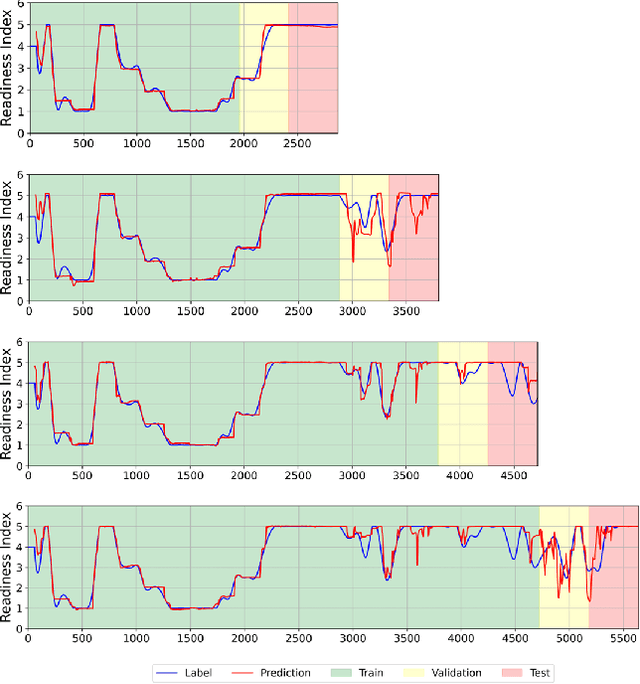
As automated driving technology advances, the role of the driver to resume control of the vehicle in conditionally automated vehicles becomes increasingly critical. In the SAE Level 3 or partly automated vehicles, the driver needs to be available and ready to intervene when necessary. This makes it essential to evaluate their readiness accurately. This article presents a comprehensive analysis of driver readiness assessment by combining head pose features and eye-tracking data. The study explores the effectiveness of predictive models in evaluating driver readiness, addressing the challenges of dataset limitations and limited ground truth labels. Machine learning techniques, including LSTM architectures, are utilised to model driver readiness based on the Spatio-temporal status of the driver's head pose and eye gaze. The experiments in this article revealed that a Bidirectional LSTM architecture, combining both feature sets, achieves a mean absolute error of 0.363 on the DMD dataset, demonstrating superior performance in assessing driver readiness. The modular architecture of the proposed model also allows the integration of additional driver-specific features, such as steering wheel activity, enhancing its adaptability and real-world applicability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge