Estimation of causal effects of multiple treatments in healthcare database studies with rare outcomes
Paper and Code
Aug 18, 2020

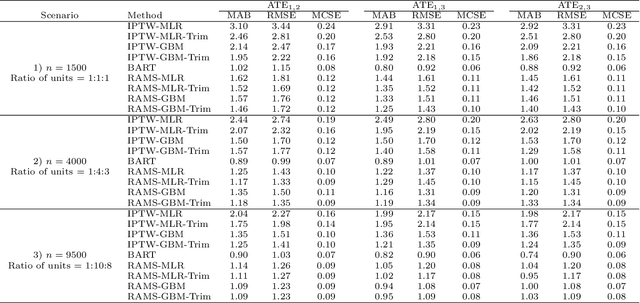
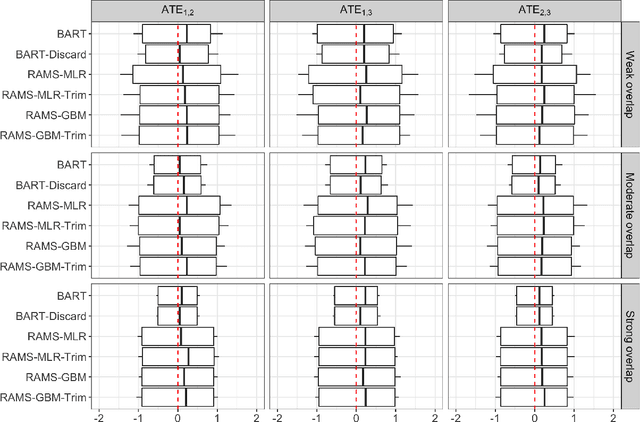
The preponderance of large-scale healthcare databases provide abundant opportunities for comparative effectiveness research. Evidence necessary to making informed treatment decisions often relies on comparing effectiveness of multiple treatment options on outcomes of interest observed in a small number of individuals. Causal inference with multiple treatments and rare outcomes is a subject that has been treated sparingly in the literature. This paper designs three sets of simulations, representative of the structure of our healthcare database study, and propose causal analysis strategies for such settings. We investigate and compare the operating characteristics of three types of methods and their variants: Bayesian Additive Regression Trees (BART), regression adjustment on multivariate spline of generalized propensity scores (RAMS) and inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) with multinomial logistic regression or generalized boosted models. Our results suggest that BART and RAMS provide lower bias and mean squared error, and the widely used IPTW methods deliver unfavorable operating characteristics. We illustrate the methods using a case study evaluating the comparative effectiveness of robotic-assisted surgery, video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery and open thoracotomy for treating non-small cell lung cancer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge