Estimating value at risk: LSTM vs. GARCH
Paper and Code
Jul 21, 2022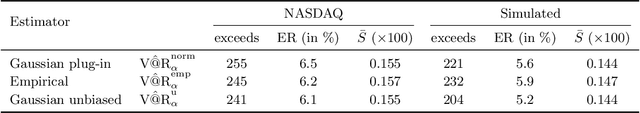
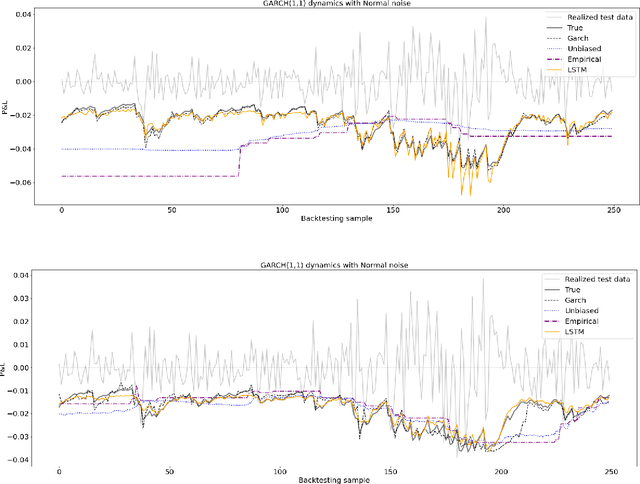
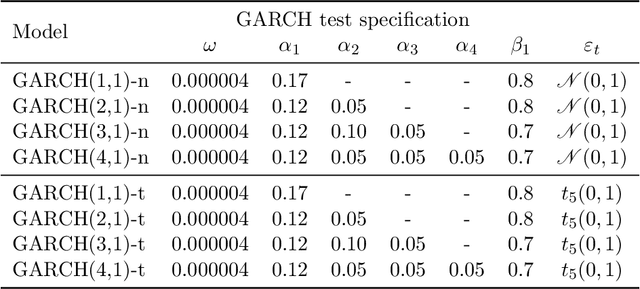

Estimating value-at-risk on time series data with possibly heteroscedastic dynamics is a highly challenging task. Typically, we face a small data problem in combination with a high degree of non-linearity, causing difficulties for both classical and machine-learning estimation algorithms. In this paper, we propose a novel value-at-risk estimator using a long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network and compare its performance to benchmark GARCH estimators. Our results indicate that even for a relatively short time series, the LSTM could be used to refine or monitor risk estimation processes and correctly identify the underlying risk dynamics in a non-parametric fashion. We evaluate the estimator on both simulated and market data with a focus on heteroscedasticity, finding that LSTM exhibits a similar performance to GARCH estimators on simulated data, whereas on real market data it is more sensitive towards increasing or decreasing volatility and outperforms all existing estimators of value-at-risk in terms of exception rate and mean quantile score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge