Entity Matching using Large Language Models
Paper and Code
Oct 17, 2023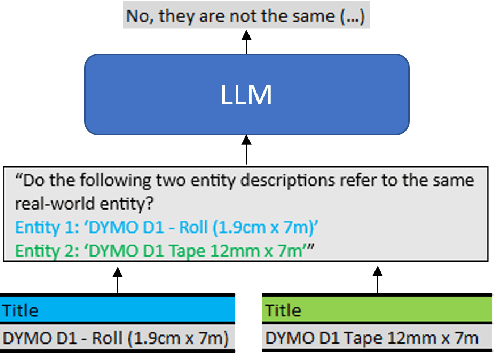
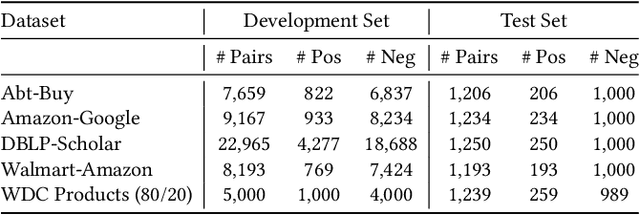
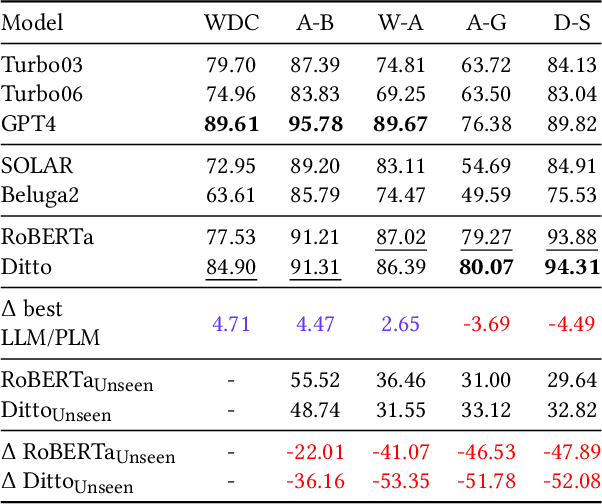
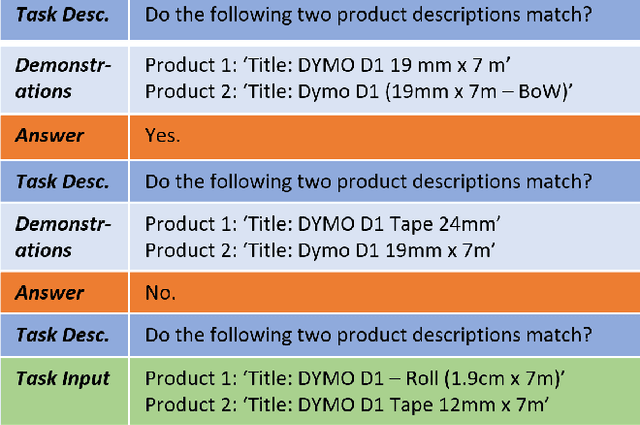
Entity Matching is the task of deciding whether two entity descriptions refer to the same real-world entity. Entity Matching is a central step in most data integration pipelines and an enabler for many e-commerce applications which require to match products offers from different vendors. State-of-the-art entity matching methods often rely on pre-trained language models (PLMs) such as BERT or RoBERTa. Two major drawbacks of these models for entity matching are that (i) the models require significant amounts of task-specific training data and (ii) the fine-tuned models are not robust concerning out-of-distribution entities. In this paper, we investigate using large language models (LLMs) for entity matching as a less domain-specific training data reliant and more robust alternative to PLM-based matchers. Our study covers hosted LLMs, such as GPT3.5 and GPT4, as well as open source LLMs based on Llama2 which can be run locally. We evaluate these models in a zero-shot scenario as well as a scenario where task-specific training data is available. We compare different prompt designs as well as the prompt sensitivity of the models in the zero-shot scenario. We investigate (i) the selection of in-context demonstrations, (ii) the generation of matching rules, as well as (iii) fine-tuning GPT3.5 in the second scenario using the same pool of training data across the different approaches. Our experiments show that GPT4 without any task-specific training data outperforms fine-tuned PLMs (RoBERTa and Ditto) on three out of five benchmark datasets reaching F1 scores around 90%. The experiments with in-context learning and rule generation show that all models beside of GPT4 benefit from these techniques (on average 5.9% and 2.2% F1), while GPT4 does not need such additional guidance in most cases...
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge