EnHDC: Ensemble Learning for Brain-Inspired Hyperdimensional Computing
Paper and Code
Mar 25, 2022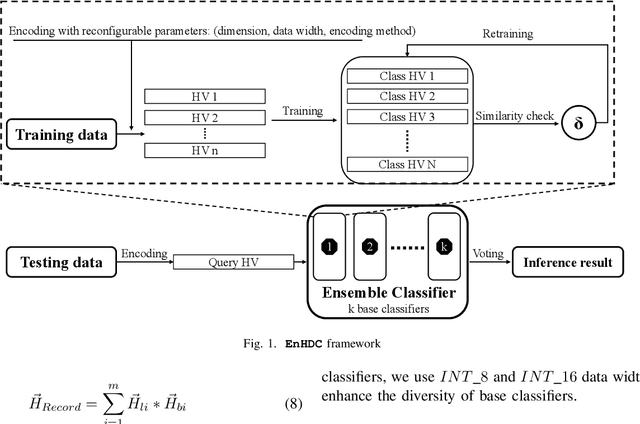
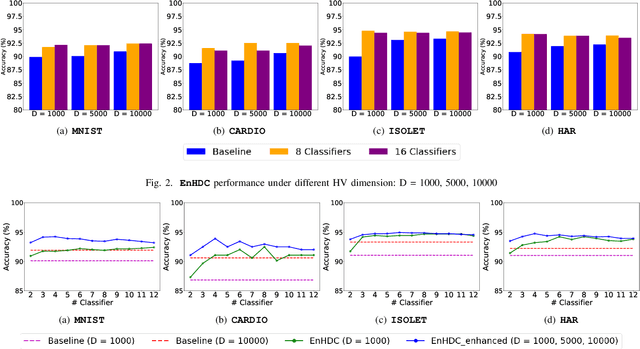
Ensemble learning is a classical learning method utilizing a group of weak learners to form a strong learner, which aims to increase the accuracy of the model. Recently, brain-inspired hyperdimensional computing (HDC) becomes an emerging computational paradigm that has achieved success in various domains such as human activity recognition, voice recognition, and bio-medical signal classification. HDC mimics the brain cognition and leverages high-dimensional vectors (e.g., 10000 dimensions) with fully distributed holographic representation and (pseudo-)randomness. This paper presents the first effort in exploring ensemble learning in the context of HDC and proposes the first ensemble HDC model referred to as EnHDC. EnHDC uses a majority voting-based mechanism to synergistically integrate the prediction outcomes of multiple base HDC classifiers. To enhance the diversity of base classifiers, we vary the encoding mechanisms, dimensions, and data width settings among base classifiers. By applying EnHDC on a wide range of applications, results show that the EnHDC can achieve on average 3.2\% accuracy improvement over a single HDC classifier. Further, we show that EnHDC with reduced dimensionality, e.g., 1000 dimensions, can achieve similar or even surpass the accuracy of baseline HDC with higher dimensionality, e.g., 10000 dimensions. This leads to a 20\% reduction of storage requirement of HDC model, which is key to enabling HDC on low-power computing platforms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge