Enhancing Generalization in Audio Deepfake Detection: A Neural Collapse based Sampling and Training Approach
Paper and Code
Apr 19, 2024
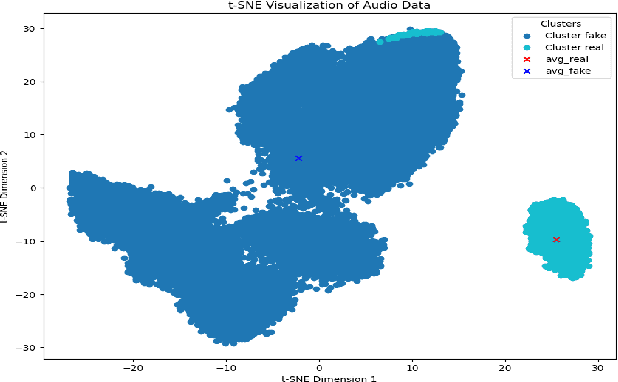

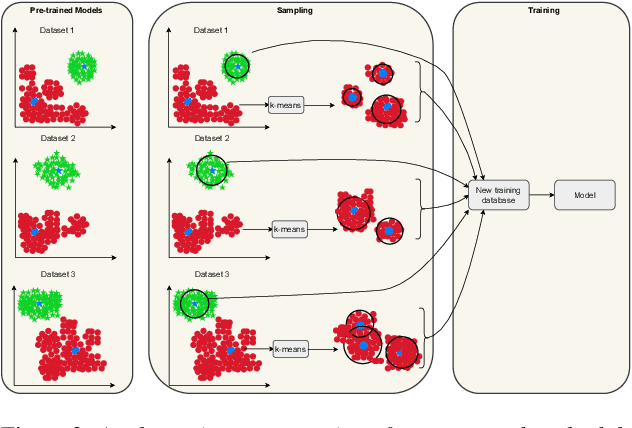
Generalization in audio deepfake detection presents a significant challenge, with models trained on specific datasets often struggling to detect deepfakes generated under varying conditions and unknown algorithms. While collectively training a model using diverse datasets can enhance its generalization ability, it comes with high computational costs. To address this, we propose a neural collapse-based sampling approach applied to pre-trained models trained on distinct datasets to create a new training database. Using ASVspoof 2019 dataset as a proof-of-concept, we implement pre-trained models with Resnet and ConvNext architectures. Our approach demonstrates comparable generalization on unseen data while being computationally efficient, requiring less training data. Evaluation is conducted using the In-the-wild dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge