Enhancing Breast Cancer Diagnosis in Mammography: Evaluation and Integration of Convolutional Neural Networks and Explainable AI
Paper and Code
Apr 09, 2024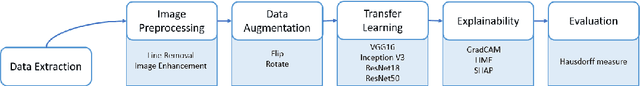
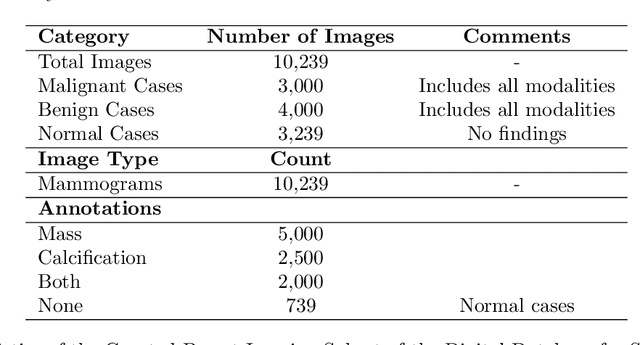
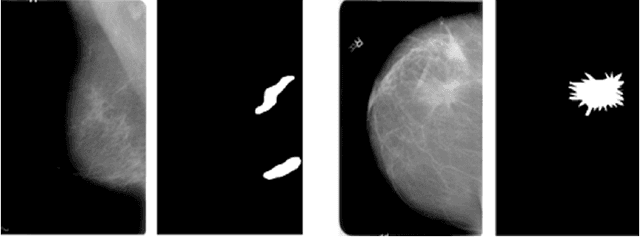
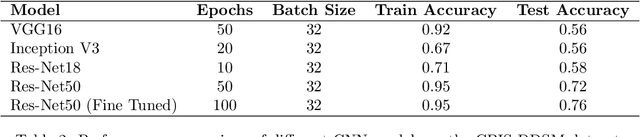
The study introduces an integrated framework combining Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) for the enhanced diagnosis of breast cancer using the CBIS-DDSM dataset. Utilizing a fine-tuned ResNet50 architecture, our investigation not only provides effective differentiation of mammographic images into benign and malignant categories but also addresses the opaque "black-box" nature of deep learning models by employing XAI methodologies, namely Grad-CAM, LIME, and SHAP, to interpret CNN decision-making processes for healthcare professionals. Our methodology encompasses an elaborate data preprocessing pipeline and advanced data augmentation techniques to counteract dataset limitations, and transfer learning using pre-trained networks, such as VGG-16, DenseNet and ResNet was employed. A focal point of our study is the evaluation of XAI's effectiveness in interpreting model predictions, highlighted by utilising the Hausdorff measure to assess the alignment between AI-generated explanations and expert annotations quantitatively. This approach plays a critical role for XAI in promoting trustworthiness and ethical fairness in AI-assisted diagnostics. The findings from our research illustrate the effective collaboration between CNNs and XAI in advancing diagnostic methods for breast cancer, thereby facilitating a more seamless integration of advanced AI technologies within clinical settings. By enhancing the interpretability of AI-driven decisions, this work lays the groundwork for improved collaboration between AI systems and medical practitioners, ultimately enriching patient care. Furthermore, the implications of our research extend well beyond the current methodologies, advocating for subsequent inquiries into the integration of multimodal data and the refinement of AI explanations to satisfy the needs of clinical practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge