Energy Storage Management via Deep Q-Networks
Paper and Code
Mar 26, 2019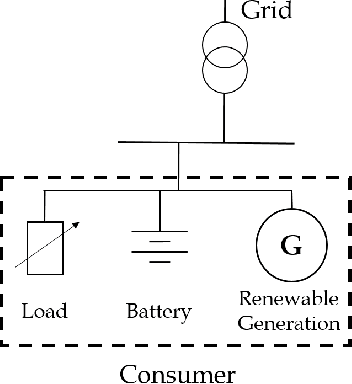
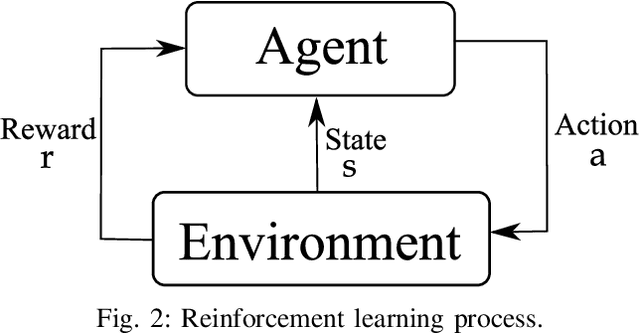
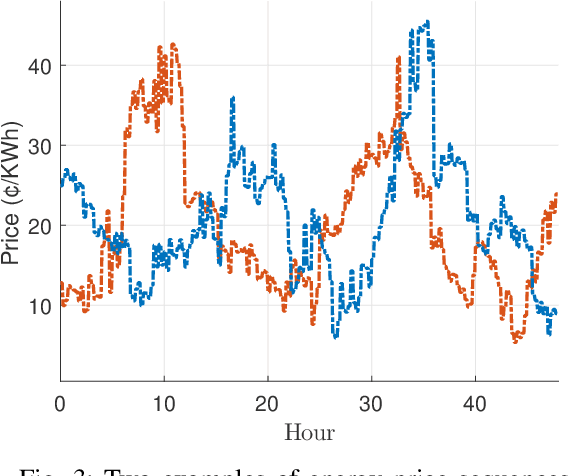
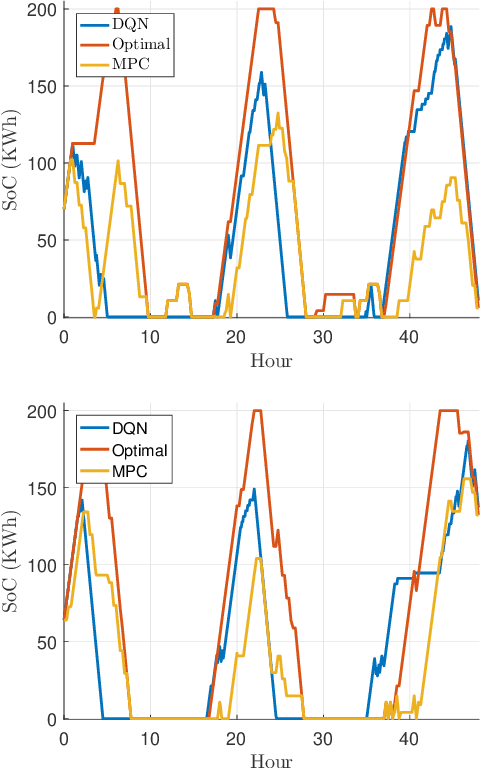
Energy storage devices represent environmentally friendly candidates to cope with volatile renewable energy generation. Motivated by the increase in privately owned storage systems, this paper studies the problem of real-time control of a storage unit co-located with a renewable energy generator and an inelastic load. Unlike many approaches in the literature, no distributional assumptions are being made on the renewable energy generation or the real-time prices. Building on the deep Q-networks algorithm, a reinforcement learning approach utilizing a neural network is devised where the storage unit operational constraints are respected. The neural network approximates the action-value function which dictates what action (charging, discharging, etc.) to take. Simulations indicate that near-optimal performance can be attained with the proposed learning-based control policy for the storage units.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge