Energy-Efficient Coverage Enhancement of Indoor THz-MISO Systems: An FD-NOMA Approach
Paper and Code
Apr 12, 2021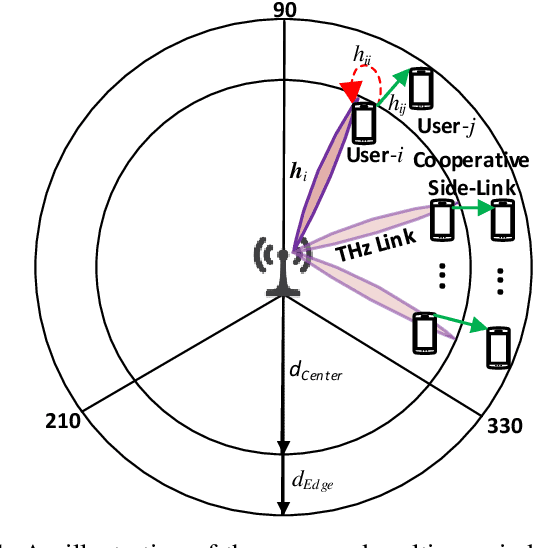
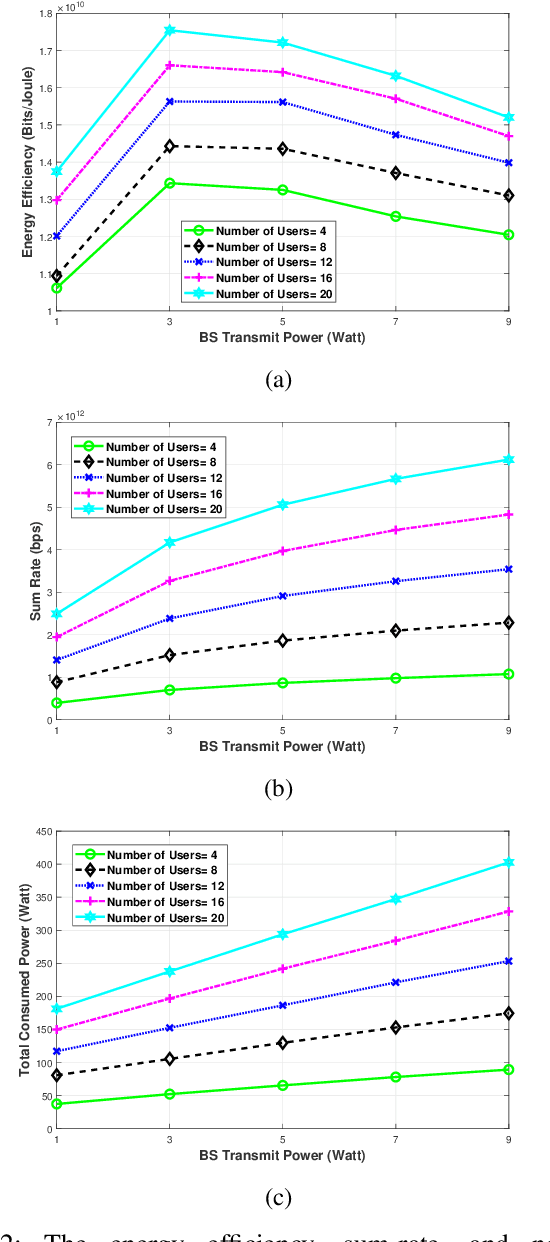
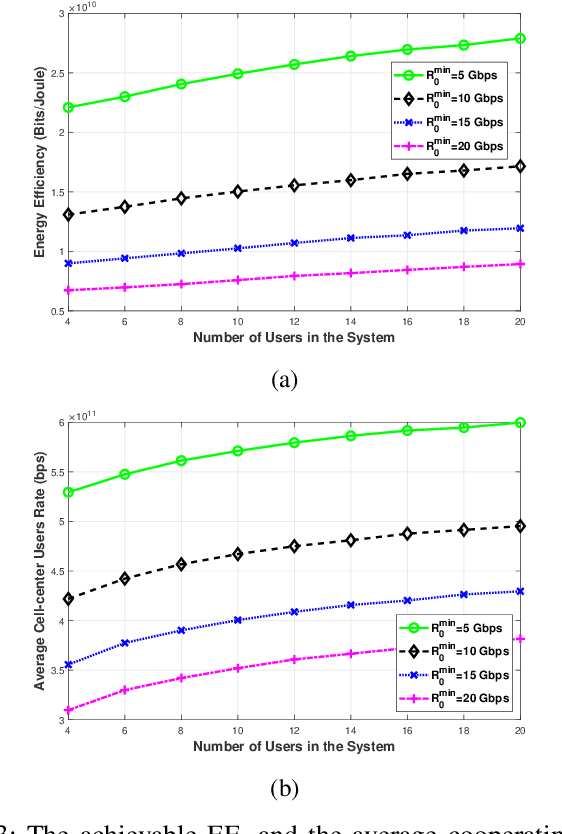
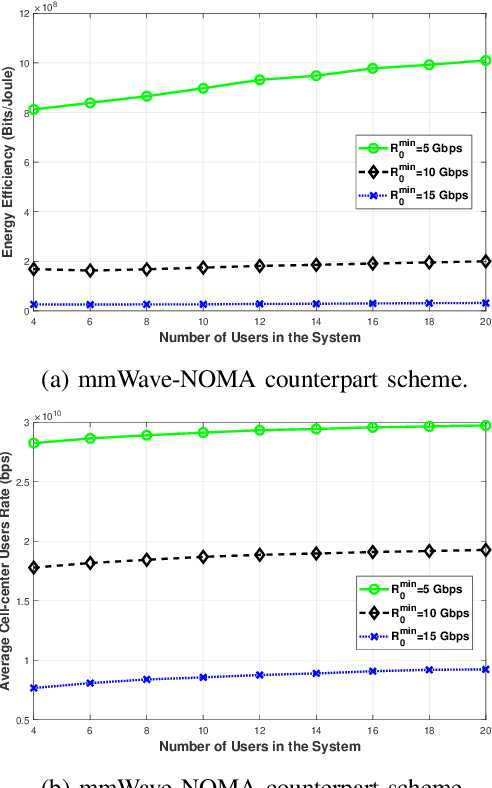
Terahertz (THz) communication is gaining more interest as one of the envisioned enablers of high-data-rate short-distance indoor applications in beyond 5G networks. Moreover, non-orthogonal multiple-access (NOMA)-enabled schemes are promising schemes to realize the target spectral efficiency, low latency, and user fairness requirements in future networks. In this paper, an energy-efficient cooperative NOMA (CNOMA) scheme that guarantees the minimum required rate for cell-edge users in an indoor THz-MISO communications network, is proposed. The proposed cooperative scheme consists of three stages: (i) beamforming stage that allocates BS beams to THz cooperating cell-center users using analog beamforming with the aid of the cosine similarity metric, (ii) user pairing stage that is tackled using the Hungarian algorithm, and (iii) a power allocation stage for the BS THz-NOMA transmit power as well as the cooperation power of the cooperating cell-center users, which is optimized in a sequential manner. The obtained results quantify the EE of the proposed scheme and shed new light on both the performance and design of multi-user THz-NOMA-enabled networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge