End-To-End Optimization of Online Neural Network-supported Two-Stage Dereverberation for Hearing Devices
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2022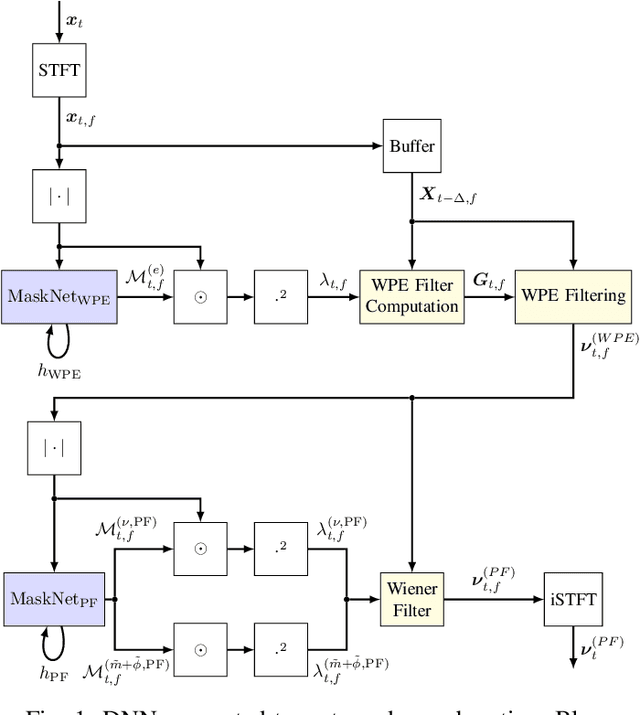
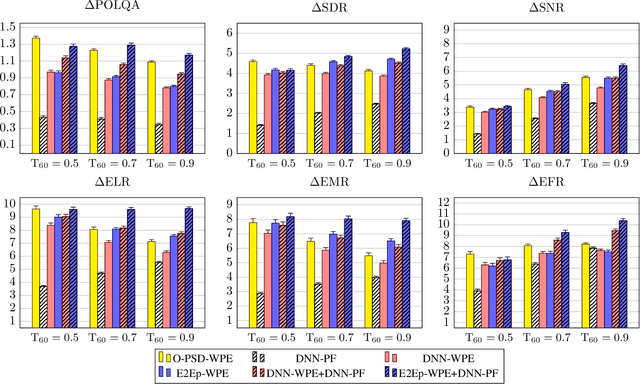
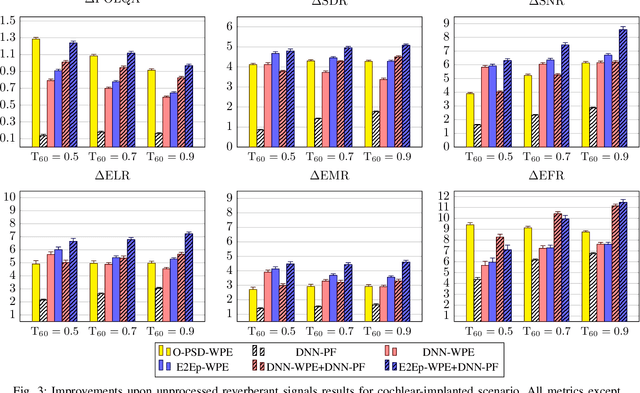
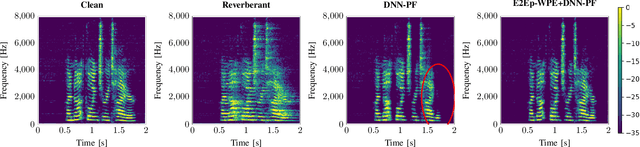
A two-stage online dereverberation algorithm for hearing devices is presented in this paper. The approach combines a multi-channel multi-frame linear filtering approach with a single-channel single-frame post-filter. Both components rely on power spectral density (PSD) estimates provided by deep neural networks (DNNs). This contribution extends our prior work, which shows that directly optimizing for a criterion at the output of the multi-channel linear filtering stage results in a more efficient dereverberation, as compared to placing the criterion at the output of the DNN to optimize the PSD estimation. In the present work, we show that the dereverberation performance of the proposed first stage particularly improves the early-to-mid reverberation ratio if trained end-to-end. We thus argue that it can be combined with a post-filtering stage which benefits from the early-to-mid ratio improvement and is consequently able to efficiently suppress the residual late reverberation. This proposed two stage procedure is shown to be both very effective in terms of dereverberation performance and computational demands. Furthermore, the proposed system can be adapted to the needs of different types of hearing-device users by controlling the amount of reduction of early reflections. The proposed system outperforms the previously proposed end-to-end DNN-supported linear filtering algorithm, as well as other traditional approaches, based on an evaluation using the noise-free version of the WHAMR! dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge