End-to-End Approach for Recognition of Historical Digit Strings
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2021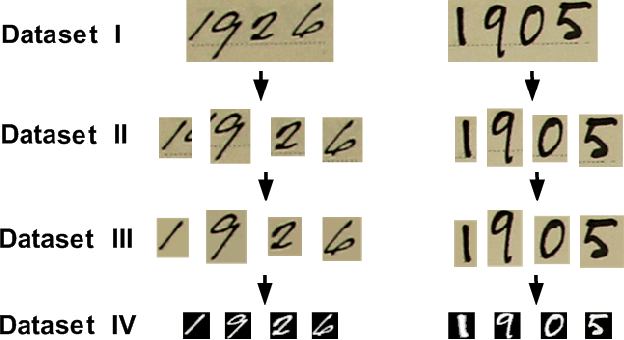
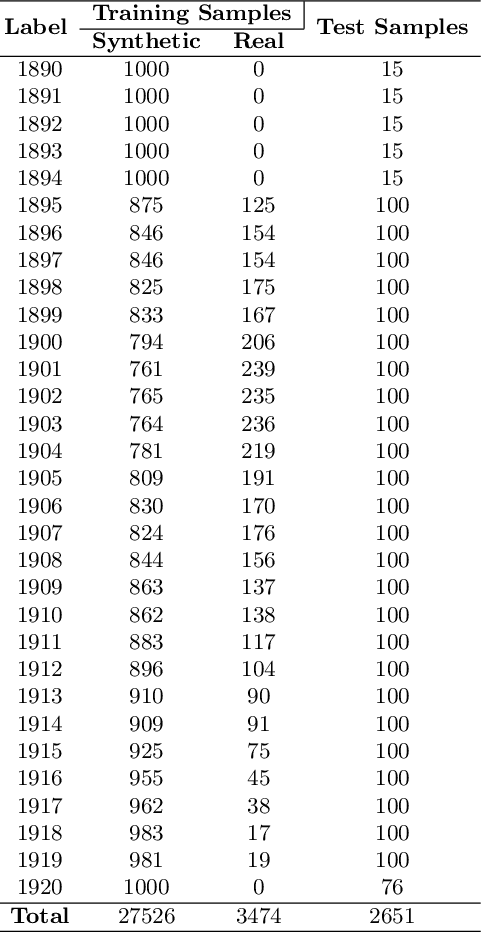
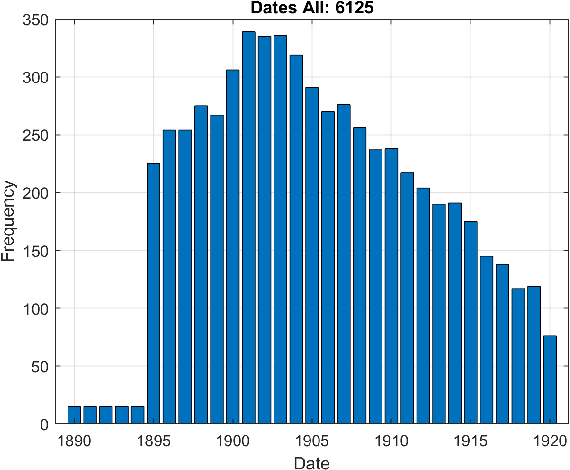

The plethora of digitalised historical document datasets released in recent years has rekindled interest in advancing the field of handwriting pattern recognition. In the same vein, a recently published data set, known as ARDIS, presents handwritten digits manually cropped from 15.000 scanned documents of Swedish church books and exhibiting various handwriting styles. To this end, we propose an end-to-end segmentation-free deep learning approach to handle this challenging ancient handwriting style of dates present in the ARDIS dataset (4-digits long strings). We show that with slight modifications in the VGG-16 deep model, the framework can achieve a recognition rate of 93.2%, resulting in a feasible solution free of heuristic methods, segmentation, and fusion methods. Moreover, the proposed approach outperforms the well-known CRNN method (a model widely applied in handwriting recognition tasks).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge