Empowering Visually Impaired Individuals: A Novel Use of Apple Live Photos and Android Motion Photos
Paper and Code
Sep 14, 2023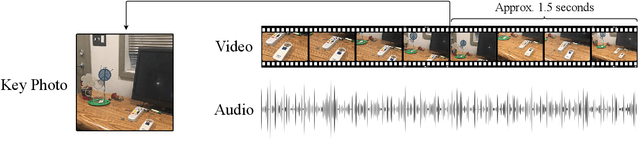


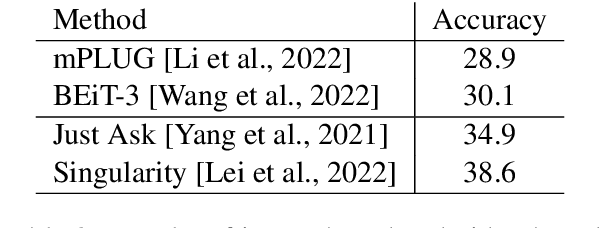
Numerous applications have been developed to assist visually impaired individuals that employ a machine learning unit to process visual input. However, a critical challenge with these applications is the sub-optimal quality of images captured by the users. Given the complexity of operating a camera for visually impaired individuals, we advocate for the use of Apple Live Photos and Android Motion Photos technologies. In this study, we introduce a straightforward methodology to evaluate and contrast the efficacy of Live/Motion Photos against traditional image-based approaches. Our findings reveal that both Live Photos and Motion Photos outperform single-frame images in common visual assisting tasks, specifically in object classification and VideoQA. We validate our results through extensive experiments on the ORBIT dataset, which consists of videos collected by visually impaired individuals. Furthermore, we conduct a series of ablation studies to delve deeper into the impact of deblurring and longer temporal crops.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge