EigenRank by Committee: A Data Subset Selection and Failure Prediction paradigm for Robust Deep Learning based Medical Image Segmentation
Paper and Code
Aug 17, 2019
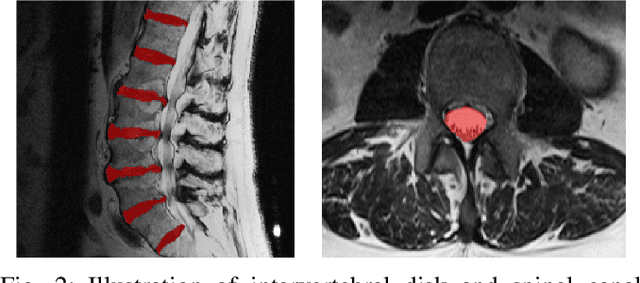
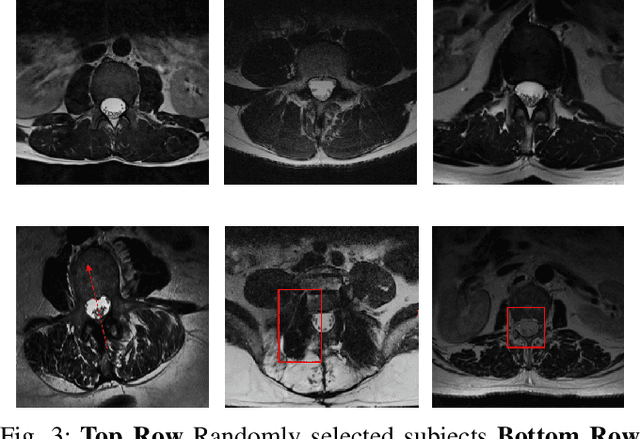
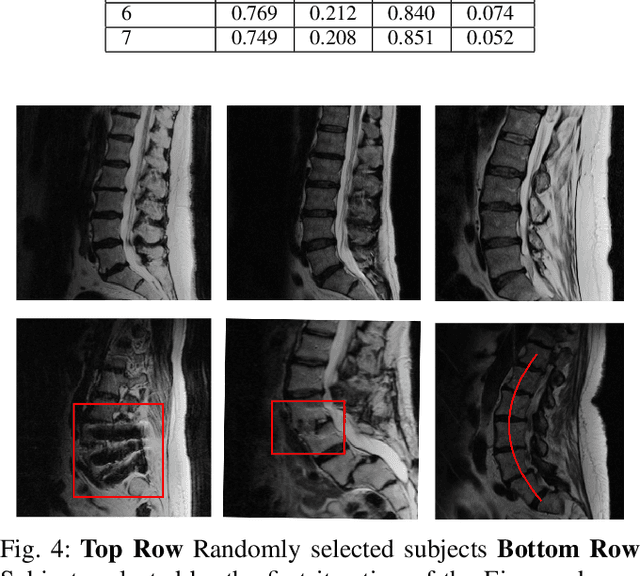
Translation of fully automated deep learning based medical image segmentation technologies to clinical workflows face two main algorithmic challenges. The first, is the collection and archival of large quantities of manually annotated ground truth data for both training and validation. The second is the relative inability of the majority of deep learning based segmentation techniques to alert physicians to a likely segmentation failure. Here we propose a novel algorithm, named `Eigenrank' which addresses both of these challenges. Eigenrank can select for manual labeling, a subset of medical images from a large database, such that a U-Net trained on this subset is superior to one trained on a randomly selected subset of the same size. Eigenrank can also be used to pick out, cases in a large database, where deep learning segmentation will fail. We present our algorithm, followed by results and a discussion of how Eigenrank exploits the Von Neumann information to perform both data subset selection and failure prediction for medical image segmentation using deep learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge