Efficient Neural Architecture for Text-to-Image Synthesis
Paper and Code
Apr 23, 2020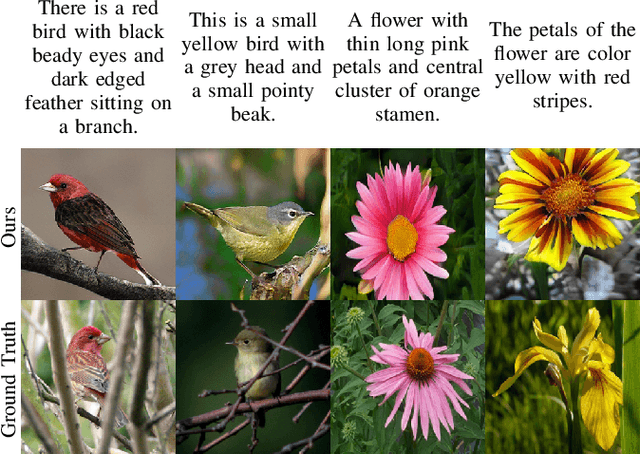
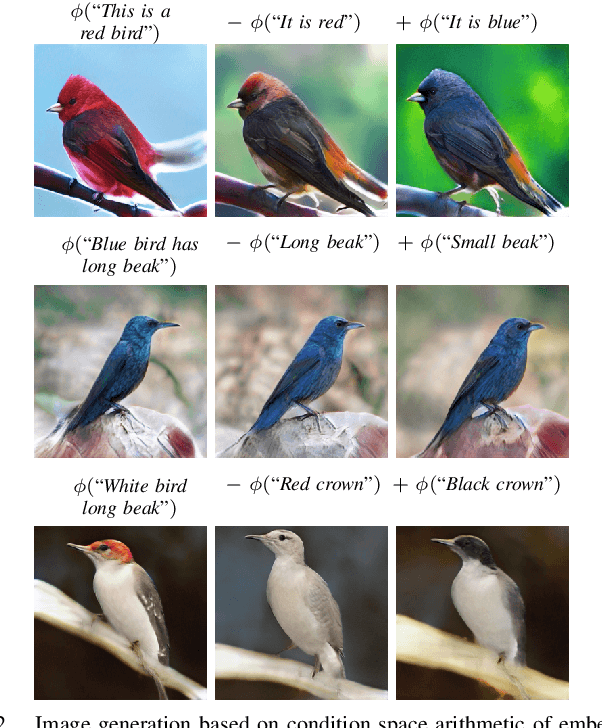



Text-to-image synthesis is the task of generating images from text descriptions. Image generation, by itself, is a challenging task. When we combine image generation and text, we bring complexity to a new level: we need to combine data from two different modalities. Most of recent works in text-to-image synthesis follow a similar approach when it comes to neural architectures. Due to aforementioned difficulties, plus the inherent difficulty of training GANs at high resolutions, most methods have adopted a multi-stage training strategy. In this paper we shift the architectural paradigm currently used in text-to-image methods and show that an effective neural architecture can achieve state-of-the-art performance using a single stage training with a single generator and a single discriminator. We do so by applying deep residual networks along with a novel sentence interpolation strategy that enables learning a smooth conditional space. Finally, our work points a new direction for text-to-image research, which has not experimented with novel neural architectures recently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge