Efficient Multi-Organ Segmentation Using SpatialConfiguration-Net with Low GPU Memory Requirements
Paper and Code
Nov 26, 2021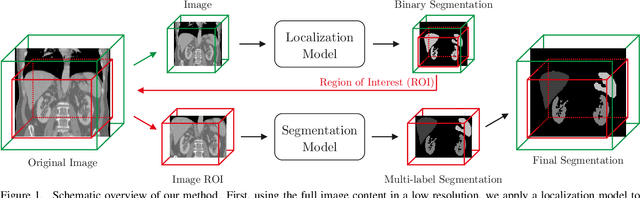

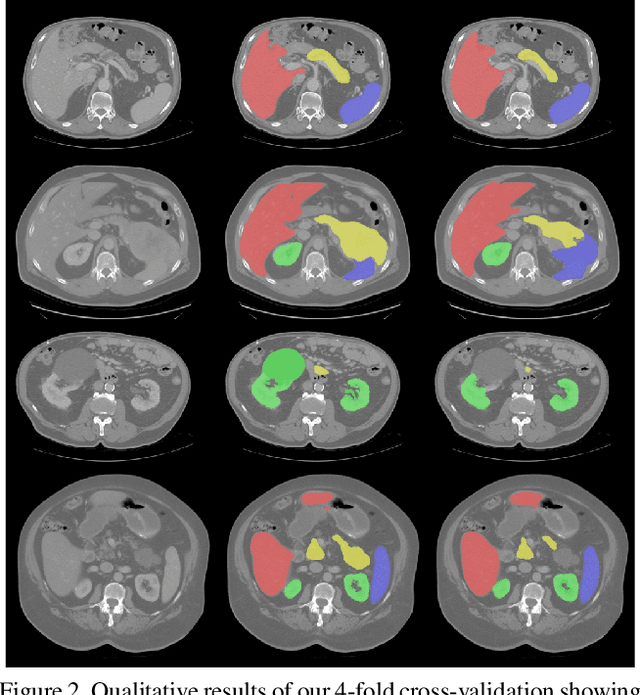
Even though many semantic segmentation methods exist that are able to perform well on many medical datasets, often, they are not designed for direct use in clinical practice. The two main concerns are generalization to unseen data with a different visual appearance, e.g., images acquired using a different scanner, and efficiency in terms of computation time and required Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) memory. In this work, we employ a multi-organ segmentation model based on the SpatialConfiguration-Net (SCN), which integrates prior knowledge of the spatial configuration among the labelled organs to resolve spurious responses in the network outputs. Furthermore, we modified the architecture of the segmentation model to reduce its memory footprint as much as possible without drastically impacting the quality of the predictions. Lastly, we implemented a minimal inference script for which we optimized both, execution time and required GPU memory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge