Efficient Image Splicing Localization via Contrastive Feature Extraction
Paper and Code
Jan 22, 2019
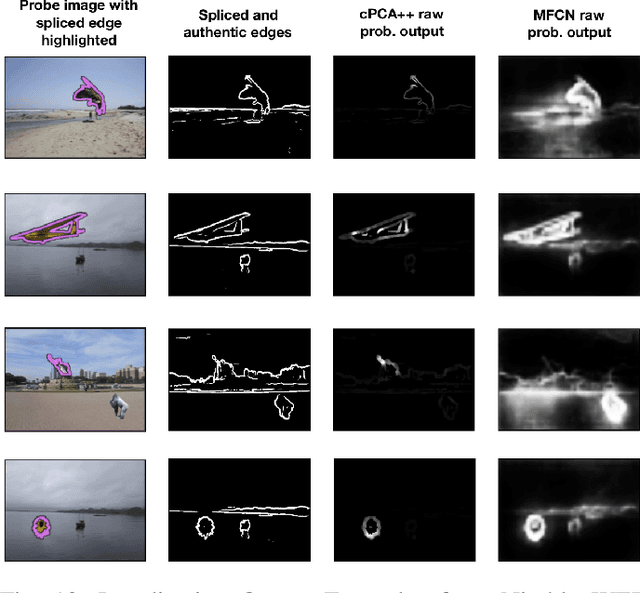

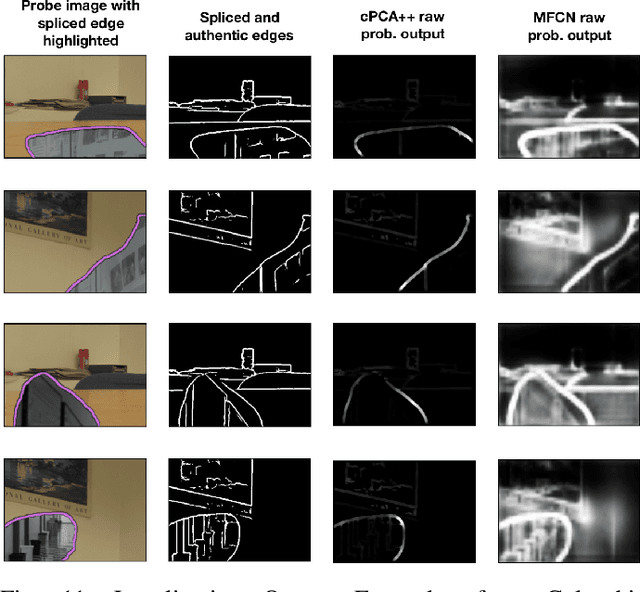

In this work, we propose a new data visualization and clustering technique for discovering discriminative structures in high-dimensional data. This technique, referred to as cPCA++, utilizes the fact that the interesting features of a "target" dataset may be obscured by high variance components during traditional PCA. By analyzing what is referred to as a "background" dataset (i.e., one that exhibits the high variance principal components but not the interesting structures), our technique is capable of efficiently highlighting the structure that is unique to the "target" dataset. Similar to another recently proposed algorithm called "contrastive PCA" (cPCA), the proposed cPCA++ method identifies important dataset specific patterns that are not detected by traditional PCA in a wide variety of settings. However, the proposed cPCA++ method is significantly more efficient than cPCA, because it does not require the parameter sweep in the latter approach. We applied the cPCA++ method to the problem of image splicing localization. In this application, we utilize authentic edges as the background dataset and the spliced edges as the target dataset. The proposed method is significantly more efficient than state-of-the-art methods, as the former does not require iterative updates of filter weights via stochastic gradient descent and backpropagation, nor the training of a classifier. Furthermore, the cPCA++ method is shown to provide performance scores comparable to the state-of-the-art Multi-task Fully Convolutional Network (MFCN).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge