Efficient Differentiable Discovery of Causal Order
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2024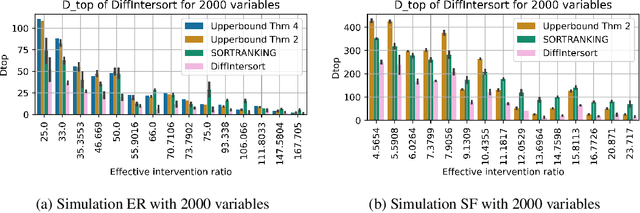
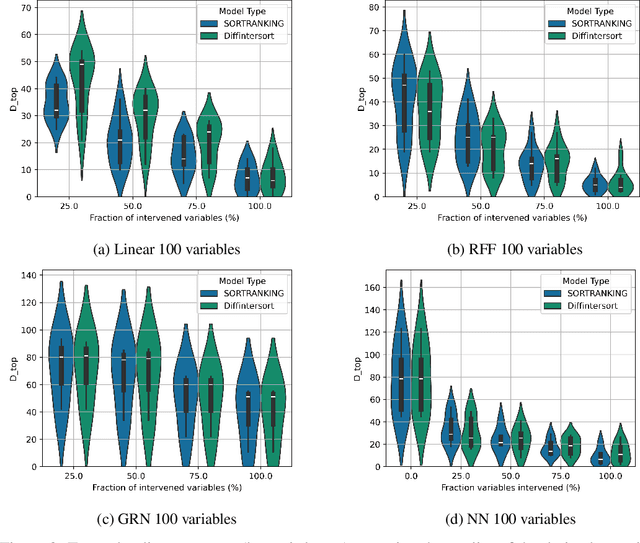
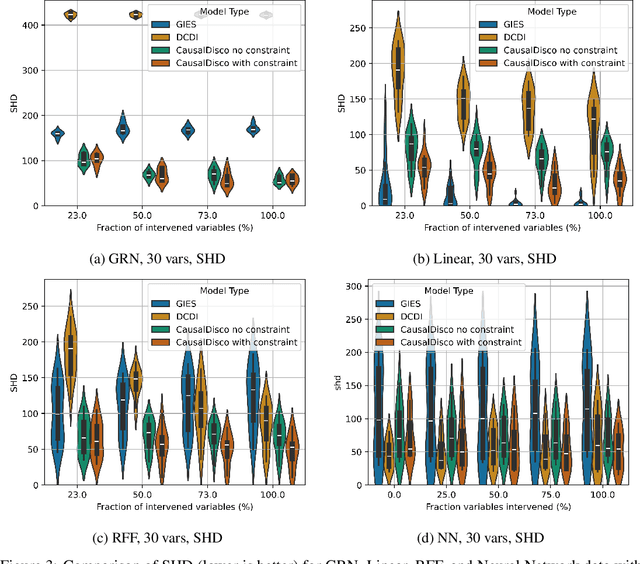
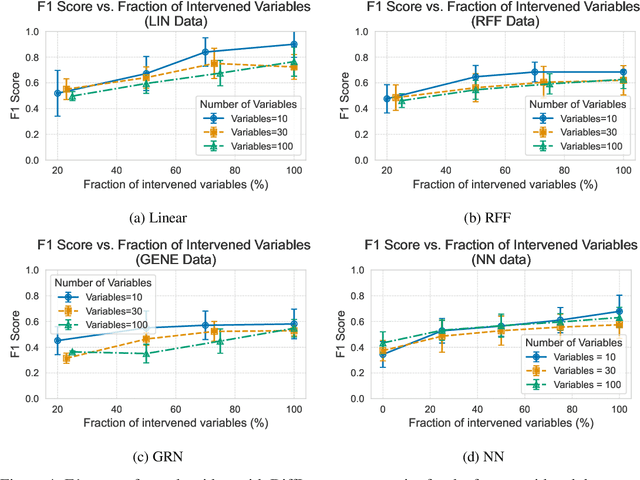
In the algorithm Intersort, Chevalley et al. (2024) proposed a score-based method to discover the causal order of variables in a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) model, leveraging interventional data to outperform existing methods. However, as a score-based method over the permutahedron, Intersort is computationally expensive and non-differentiable, limiting its ability to be utilised in problems involving large-scale datasets, such as those in genomics and climate models, or to be integrated into end-to-end gradient-based learning frameworks. We address this limitation by reformulating Intersort using differentiable sorting and ranking techniques. Our approach enables scalable and differentiable optimization of causal orderings, allowing the continuous score function to be incorporated as a regularizer in downstream tasks. Empirical results demonstrate that causal discovery algorithms benefit significantly from regularizing on the causal order, underscoring the effectiveness of our method. Our work opens the door to efficiently incorporating regularization for causal order into the training of differentiable models and thereby addresses a long-standing limitation of purely associational supervised learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge