Efficient Cloud Pipelines for Neural Radiance Fields
Paper and Code
Nov 03, 2023
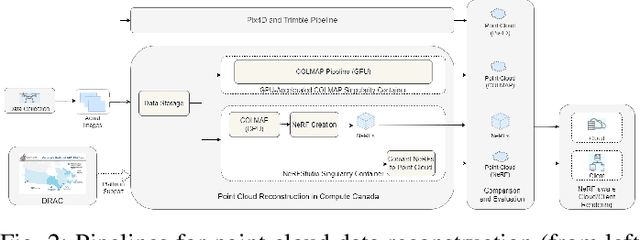
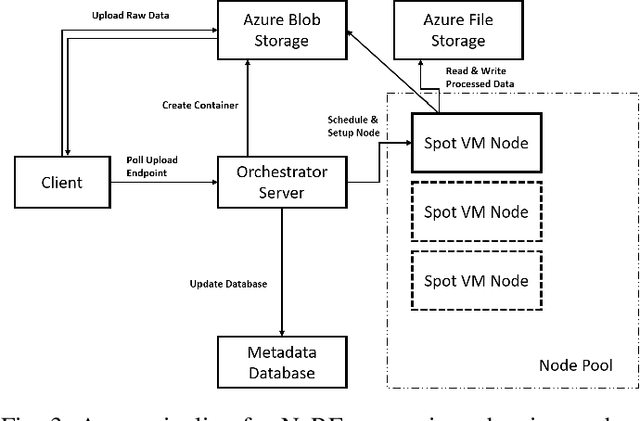
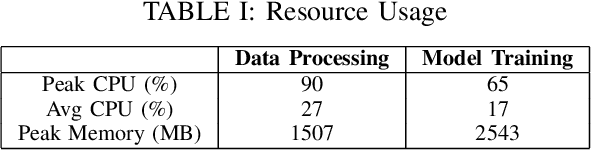
Since their introduction in 2020, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have taken the computer vision community by storm. They provide a multi-view representation of a scene or object that is ideal for eXtended Reality (XR) applications and for creative endeavors such as virtual production, as well as change detection operations in geospatial analytics. The computational cost of these generative AI models is quite high, however, and the construction of cloud pipelines to generate NeRFs is neccesary to realize their potential in client applications. In this paper, we present pipelines on a high performance academic computing cluster and compare it with a pipeline implemented on Microsoft Azure. Along the way, we describe some uses of NeRFs in enabling novel user interaction scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge