Efficient and Private: Memorisation under differentially private parameter-efficient fine-tuning in language models
Paper and Code
Nov 24, 2024
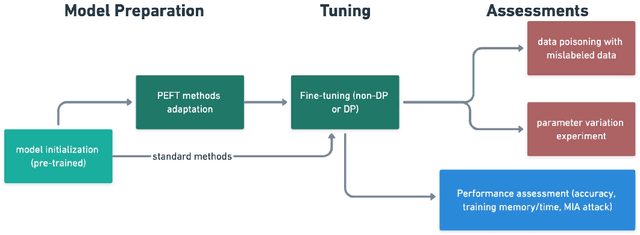
Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) for specific tasks introduces privacy risks, as models may inadvertently memorise and leak sensitive training data. While Differential Privacy (DP) offers a solution to mitigate these risks, it introduces significant computational and performance trade-offs, particularly with standard fine-tuning approaches. Previous work has primarily focused on full-parameter updates, which are computationally intensive and may not fully leverage DPs potential in large models. In this work, we address these shortcomings by investigating Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods under DP constraints. We show that PEFT methods achieve comparable performance to standard fine-tuning while requiring fewer parameters and significantly reducing privacy leakage. Furthermore, we incorporate a data poisoning experiment involving intentional mislabelling to assess model memorisation and directly measure privacy risks. Our findings indicate that PEFT methods not only provide a promising alternative but also serve as a complementary approach for privacy-preserving, resource-efficient fine-tuning of LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge