E2EG: End-to-End Node Classification Using Graph Topology and Text-based Node Attributes
Paper and Code
Aug 09, 2022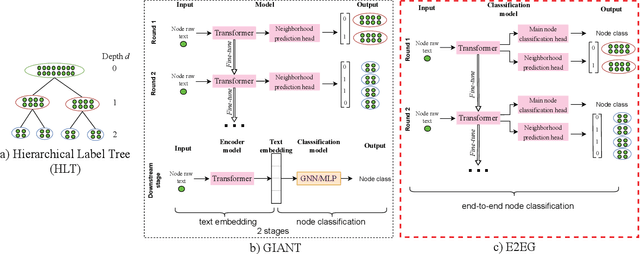
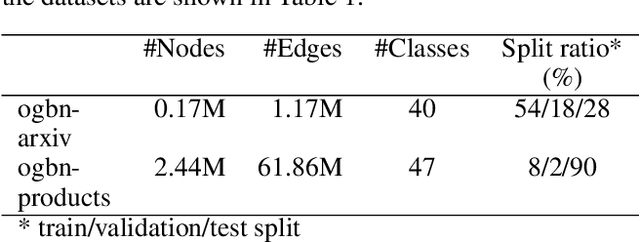
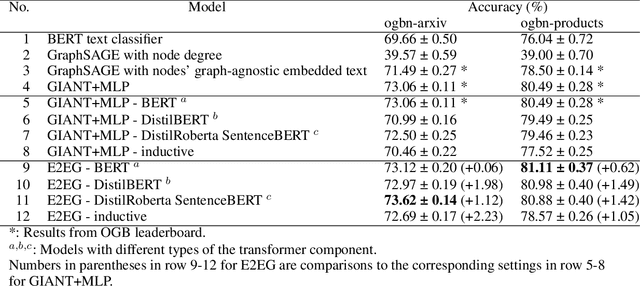
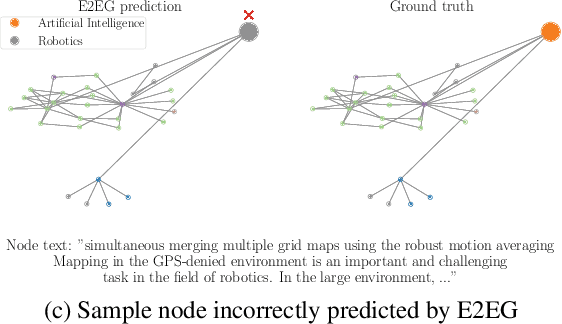
Node classification utilizing text-based node attributes has many real-world applications, ranging from prediction of paper topics in academic citation graphs to classification of user characteristics in social media networks. State-of-the-art node classification frameworks, such as GIANT, use a two-stage pipeline: first embedding the text attributes of graph nodes then feeding the resulting embeddings into a node classification model. In this paper, we eliminate these two stages and instead develop an end-to-end node classification model that builds upon GIANT, called End-to-End-GIANT (E2EG). The tandem utilization of a main and an auxiliary classification objectives in our approach results in a more robust model, thus enabling the BERT backbone to be switched out for a distilled encoder with a 25% - 40% reduction in the number of parameters. Moreover, the end-to-end nature of the model increases ease of use, as it avoids the need of chaining multiple models for node classification. Compared to a GIANT+MLP baseline on the ogbn-arxiv and ogbn-products datasets, our model is able to obtain slightly better accuracy in the transductive setting (+0.5%), while reducing model training time by up to 40%. Our model is also applicable in the inductive setting, outperforming GIANT+MLP by up to +2.23%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge