Dual-Frequency Radar Wave-Inversion for Sub-Surface Material Characterization
Paper and Code
Mar 28, 2024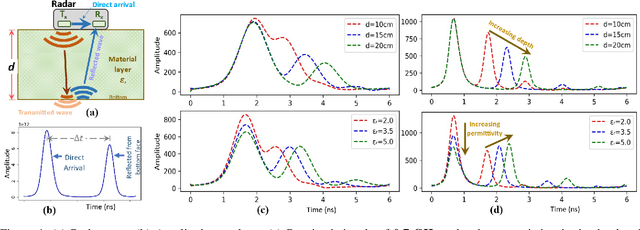


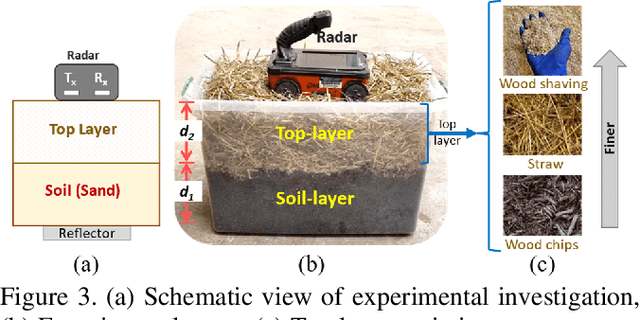
Moisture estimation of sub-surface soil and the overlaying biomass layer is pivotal in precision agriculture and wildfire risk assessment. However, the characterization of layered material is nontrivial due to the radar penetration-resolution tradeoff. Here, a waveform inversion-based method was proposed for predicting the dielectric permittivity (as a moisture proxy) of the bottom soil layer and the top biomass layer from radar signals. Specifically, the use of a combination of a higher and a lower frequency radar compared to a single frequency in predicting the permittivity of both the soil and the overlaying layer was investigated in this study. The results show that each layer was best characterized via one of the frequencies. However, for the simultaneous prediction of both layers permittivity, the most consistent results were achieved by inversion of data from a combination of both frequencies, showing better correlation with in situ permittivity and reduced prediction errors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge