Dropout as data augmentation
Paper and Code
Jan 08, 2016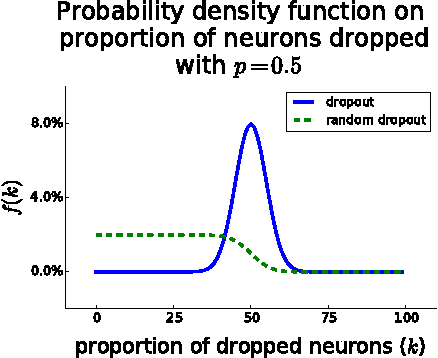
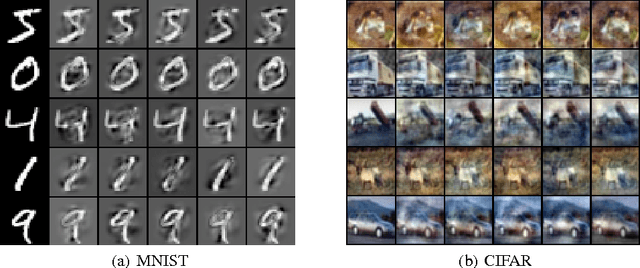

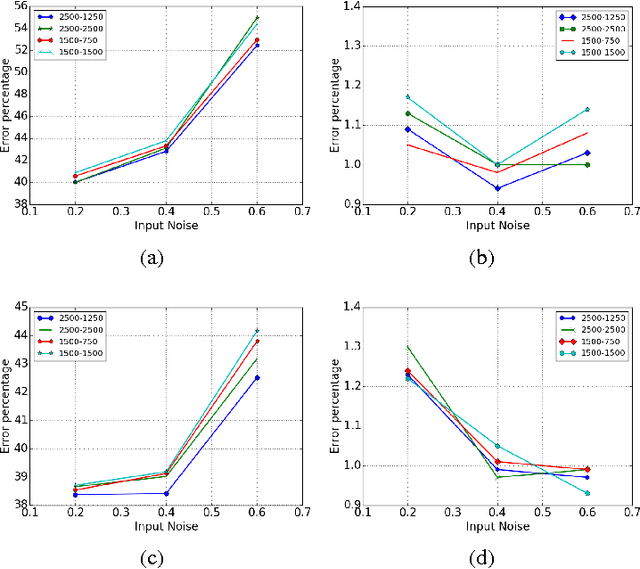
Dropout is typically interpreted as bagging a large number of models sharing parameters. We show that using dropout in a network can also be interpreted as a kind of data augmentation in the input space without domain knowledge. We present an approach to projecting the dropout noise within a network back into the input space, thereby generating augmented versions of the training data, and we show that training a deterministic network on the augmented samples yields similar results. Finally, we propose a new dropout noise scheme based on our observations and show that it improves dropout results without adding significant computational cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge