Drones Practicing Mechanics
Paper and Code
Jan 20, 2022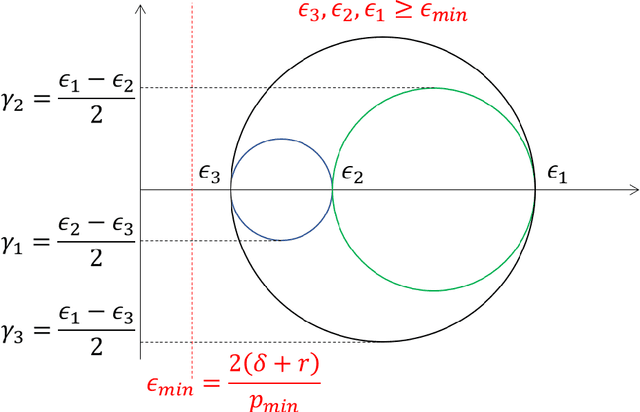
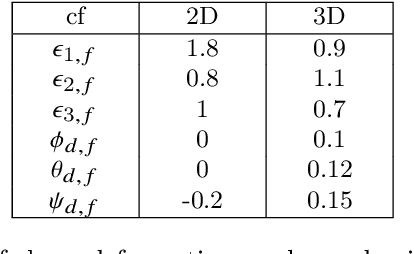
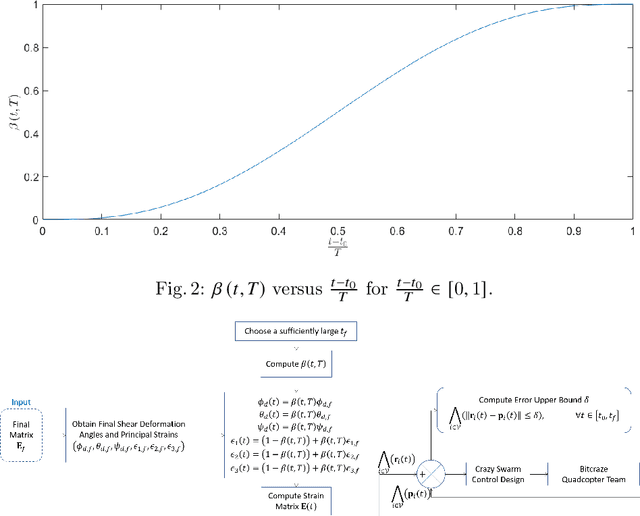
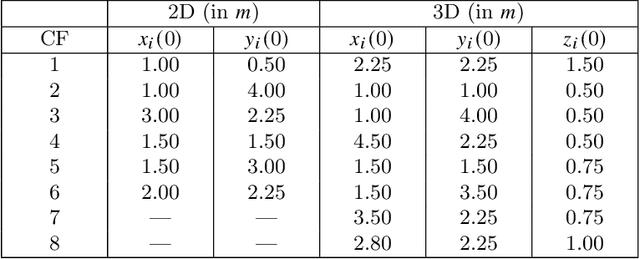
Mechanics of materials is a classic course of engineering presenting the fundamentals of strain and stress analysis to junior undergraduate students in several engineering majors. So far, material deformation and strain have been only analyzed using theoretical and numerical approaches, and they have been experimentally validated by expensive machines and tools. This paper presents a novel approach for strain and deformation analysis by using quadcopters. We propose to treat quadcopters as finite number of particles of a deformable body and apply the principles of continuum mechanics to illustrate the concept of axial and shear deformation by using quadcopter hardware in a $3$-D motion space. The outcome of this work can have significant impact on undergraduate education by filling the gap between in-class learning and hardware realization and experiments, where we introduce new roles for drones as "teachers" providing a great opportunity for practicing theoretical concepts of mechanics in a fruitful and understandable way.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge