Does Incomplete Syntax Influence Korean Language Model? Focusing on Word Order and Case Markers
Paper and Code
Jul 12, 2024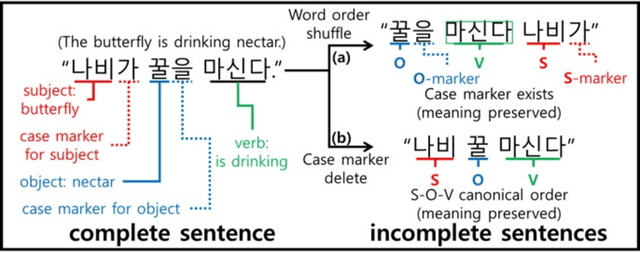
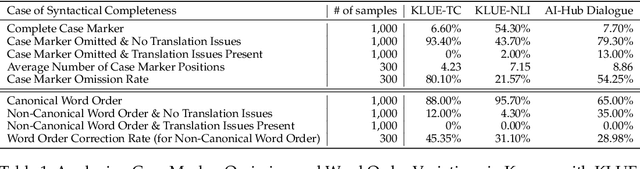

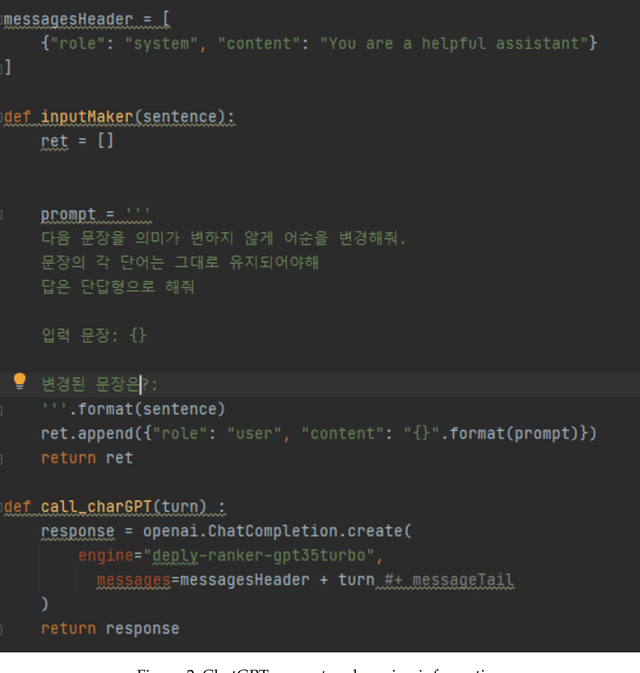
Syntactic elements, such as word order and case markers, are fundamental in natural language processing. Recent studies show that syntactic information boosts language model performance and offers clues for people to understand their learning mechanisms. Unlike languages with a fixed word order such as English, Korean allows for varied word sequences, despite its canonical structure, due to case markers that indicate the functions of sentence components. This study explores whether Korean language models can accurately capture this flexibility. We note that incomplete word orders and omitted case markers frequently appear in ordinary Korean communication. To investigate this further, we introduce the Syntactically Incomplete Korean (SIKO) dataset. Through SIKO, we assessed Korean language models' flexibility with incomplete syntax and confirmed the dataset's training value. Results indicate these models reflect Korean's inherent flexibility, accurately handling incomplete inputs. Moreover, fine-tuning with SIKO enhances the ability to handle common incomplete Korean syntactic forms. The dataset's simple construction process, coupled with significant performance enhancements, solidifies its standing as an effective data augmentation technique.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge