Disentangling Active and Passive Cosponsorship in the U.S. Congress
Paper and Code
May 19, 2022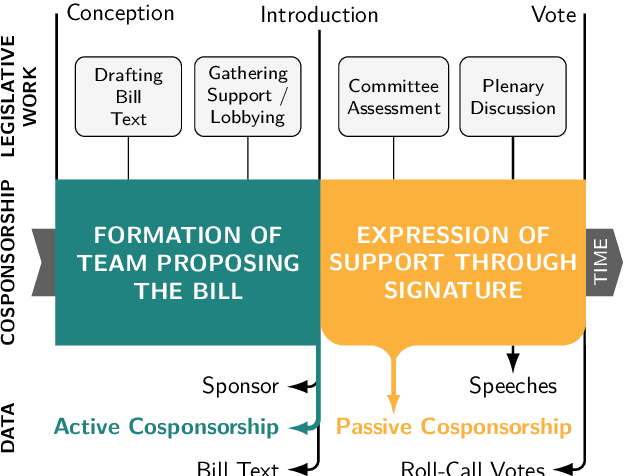
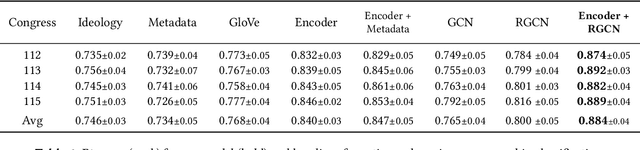
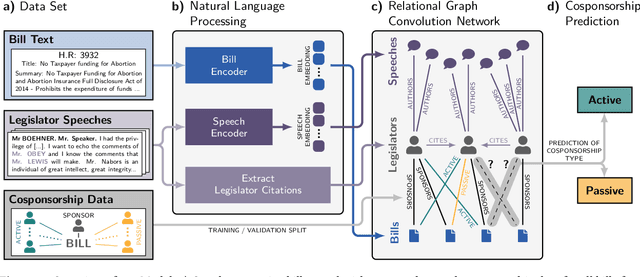
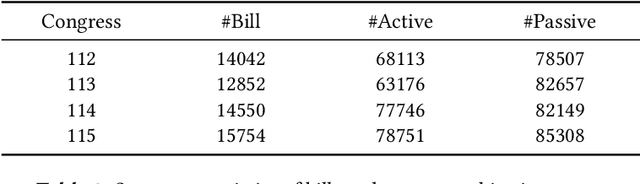
In the U.S. Congress, legislators can use active and passive cosponsorship to support bills. We show that these two types of cosponsorship are driven by two different motivations: the backing of political colleagues and the backing of the bill's content. To this end, we develop an Encoder+RGCN based model that learns legislator representations from bill texts and speech transcripts. These representations predict active and passive cosponsorship with an F1-score of 0.88. Applying our representations to predict voting decisions, we show that they are interpretable and generalize to unseen tasks.
* 20 pages, 10 figures, 6 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge