Discriminative and Generative Transformer-based Models For Situation Entity Classification
Paper and Code
Sep 15, 2021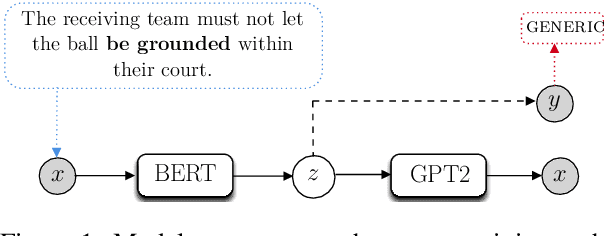
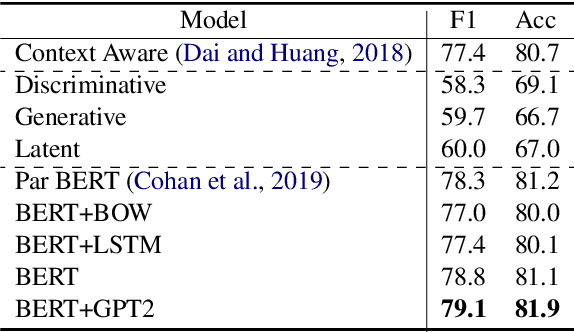
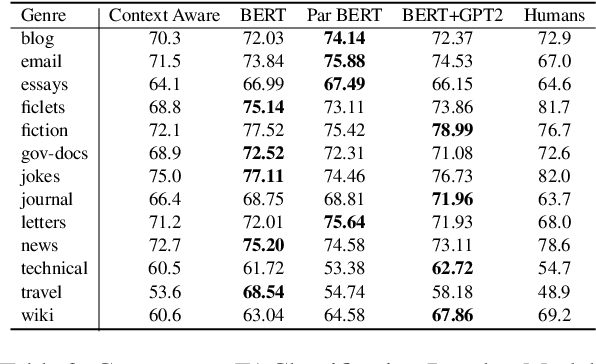
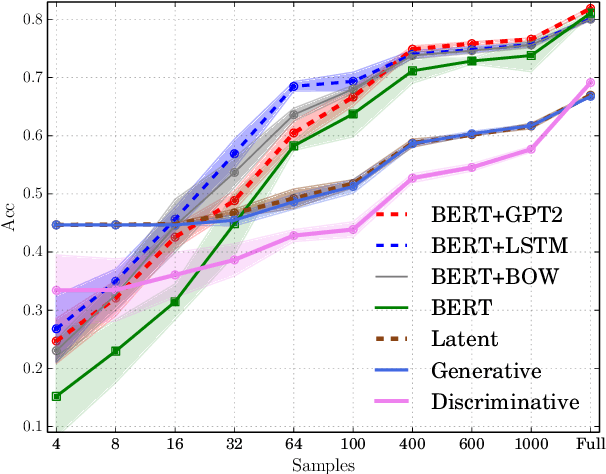
We re-examine the situation entity (SE) classification task with varying amounts of available training data. We exploit a Transformer-based variational autoencoder to encode sentences into a lower dimensional latent space, which is used to generate the text and learn a SE classifier. Test set and cross-genre evaluations show that when training data is plentiful, the proposed model can improve over the previous discriminative state-of-the-art models. Our approach performs disproportionately better with smaller amounts of training data, but when faced with extremely small sets (4 instances per label), generative RNN methods outperform transformers. Our work provides guidance for future efforts on SE and semantic prediction tasks, and low-label training regimes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge