Disambiguatory Signals are Stronger in Word-initial Positions
Paper and Code
Feb 03, 2021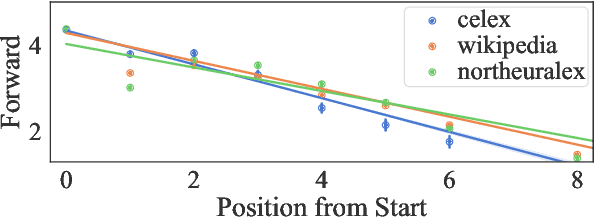
Psycholinguistic studies of human word processing and lexical access provide ample evidence of the preferred nature of word-initial versus word-final segments, e.g., in terms of attention paid by listeners (greater) or the likelihood of reduction by speakers (lower). This has led to the conjecture -- as in Wedel et al. (2019b), but common elsewhere -- that languages have evolved to provide more information earlier in words than later. Information-theoretic methods to establish such tendencies in lexicons have suffered from several methodological shortcomings that leave open the question of whether this high word-initial informativeness is actually a property of the lexicon or simply an artefact of the incremental nature of recognition. In this paper, we point out the confounds in existing methods for comparing the informativeness of segments early in the word versus later in the word, and present several new measures that avoid these confounds. When controlling for these confounds, we still find evidence across hundreds of languages that indeed there is a cross-linguistic tendency to front-load information in words.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge