Directly Training Joint Energy-Based Models for Conditional Synthesis and Calibrated Prediction of Multi-Attribute Data
Paper and Code
Jul 19, 2021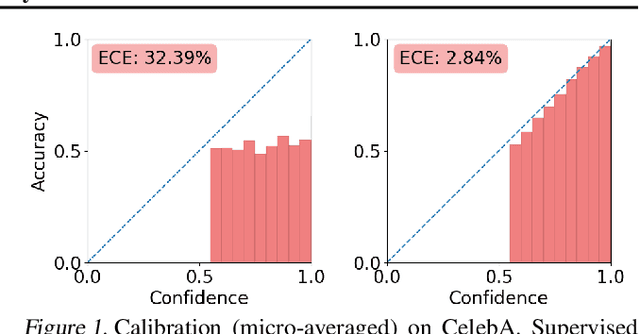
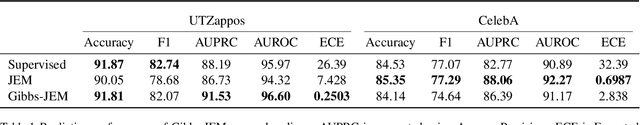
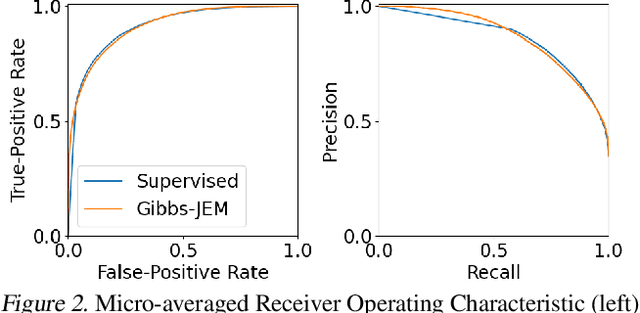
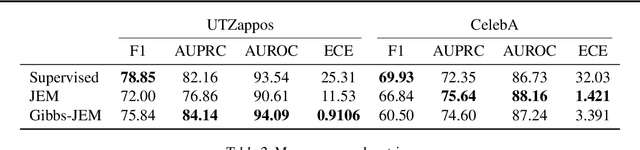
Multi-attribute classification generalizes classification, presenting new challenges for making accurate predictions and quantifying uncertainty. We build upon recent work and show that architectures for multi-attribute prediction can be reinterpreted as energy-based models (EBMs). While existing EBM approaches achieve strong discriminative performance, they are unable to generate samples conditioned on novel attribute combinations. We propose a simple extension which expands the capabilities of EBMs to generating accurate conditional samples. Our approach, combined with newly developed techniques in energy-based model training, allows us to directly maximize the likelihood of data and labels under the unnormalized joint distribution. We evaluate our proposed approach on high-dimensional image data with high-dimensional binary attribute labels. We find our models are capable of both accurate, calibrated predictions and high-quality conditional synthesis of novel attribute combinations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge