Direct Multi-hop Attention based Graph Neural Network
Paper and Code
Oct 02, 2020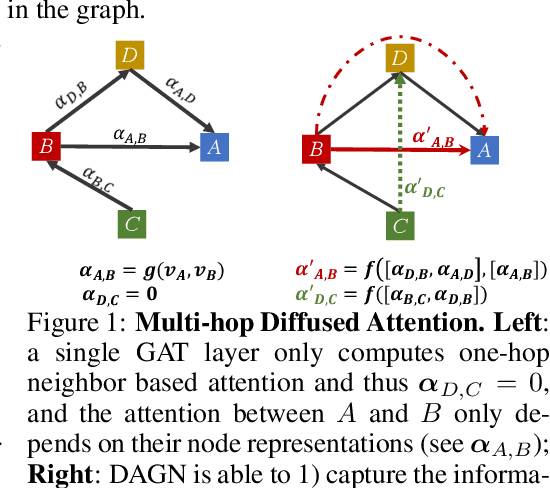
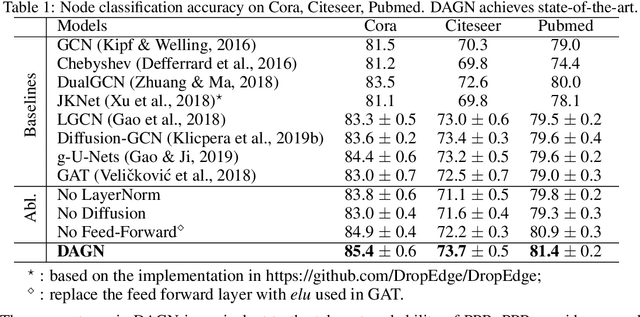
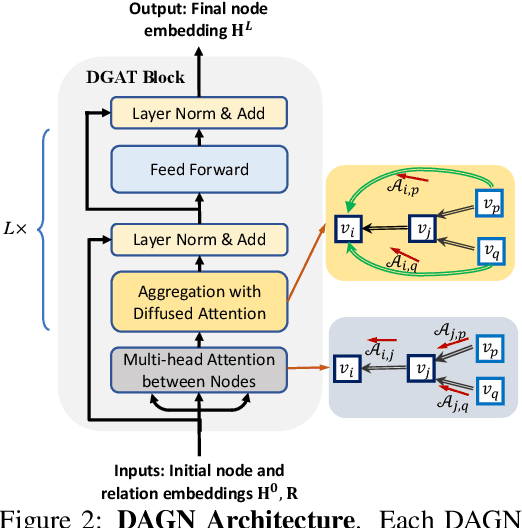
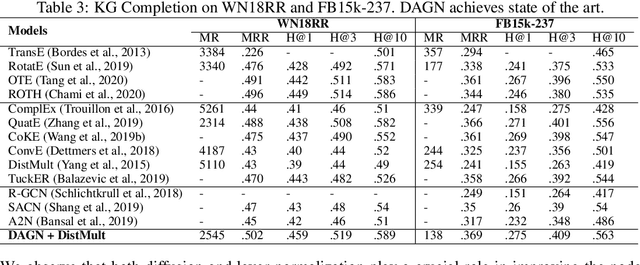
Introducing self-attention mechanism in graph neural networks (GNNs) achieved state-of-the-art performance for graph representation learning. However, at every layer, attention is only computed between two connected nodes and depends solely on the representation of both nodes. This attention computation cannot account for the multi-hop neighbors which supply graph structure context information and have influence on the node representation learning as well. In this paper, we propose Direct Multi-hop Attention based Graph neural Network (DAGN) for graph representation learning, a principled way to incorporate multi-hop neighboring context into attention computation, enabling long-range interactions at every layer. To compute attention between nodes that are multiple hops away, DAGN diffuses the attention scores from neighboring nodes to non-neighboring nodes, thus increasing the receptive field for every message passing layer. Unlike previous methods, DAGN uses a diffusion prior on attention values, to efficiently account for all paths between the pair of nodes when computing multi-hop attention weights. This helps DAGN capture large-scale structural information in a single layer, and learn more informative attention distribution. Experimental results on standard semi-supervised node classification as well as the knowledge graph completion show that DAGN achieves state-of-the-art results: DAGN achieves up to 5.7% relative error reduction over the previous state-of-the-art on Cora, Citeseer, and Pubmed. DAGN also obtains the best performance on a large-scale Open Graph Benchmark dataset. On knowledge graph completion DAGN advances state-of-the-art on WN18RR and FB15k-237 across four different performance metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge