DiffLoop: Tuning PID controllers by differentiating through the feedback loop
Paper and Code
Jun 19, 2021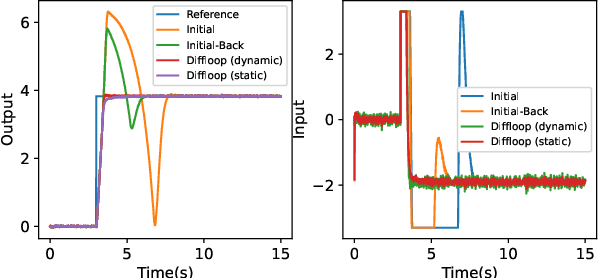
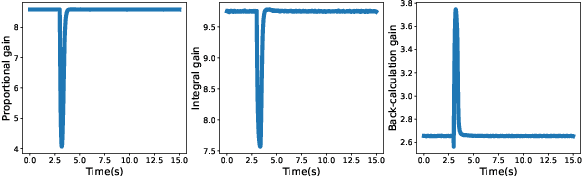
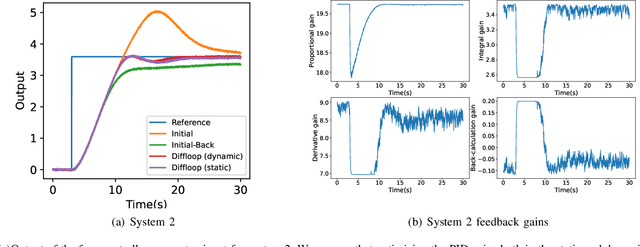
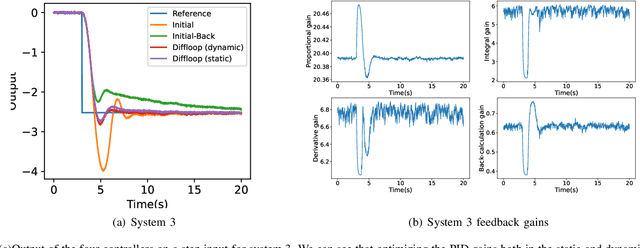
Since most industrial control applications use PID controllers, PID tuning and anti-windup measures are significant problems. This paper investigates tuning the feedback gains of a PID controller via back-calculation and automatic differentiation tools. In particular, we episodically use a cost function to generate gradients and perform gradient descent to improve controller performance. We provide a theoretical framework for analyzing this non-convex optimization and establish a relationship between back-calculation and disturbance feedback policies. We include numerical experiments on linear systems with actuator saturation to show the efficacy of this approach.
* Extension of paper in 2021 55th Annual Conference on Information
Sciences and Systems (CISS). IEEE, 2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge