Differentiable Artificial Reverberation
Paper and Code
May 28, 2021
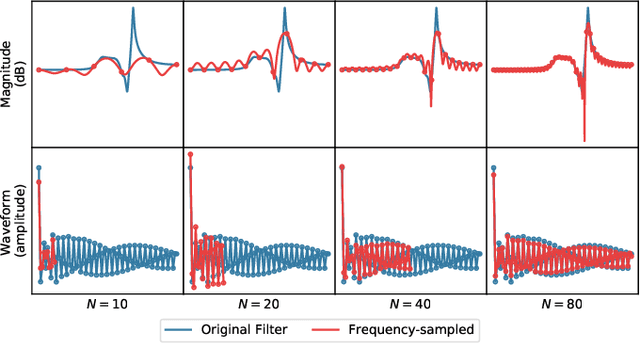

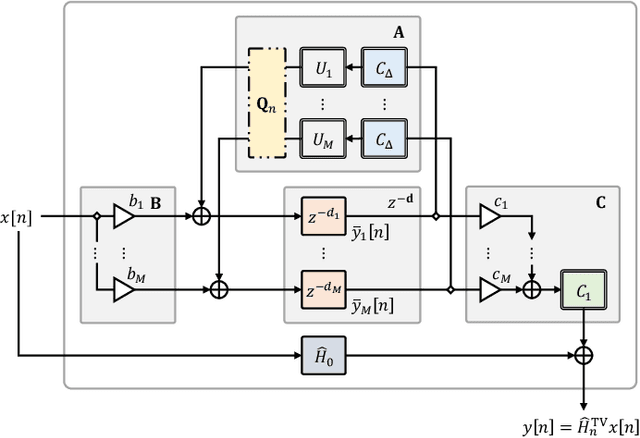
We propose differentiable artificial reverberation (DAR), a family of artificial reverberation (AR) models implemented in a deep learning framework. Combined with the modern deep neural networks (DNNs), the differentiable structure of DAR allows training loss gradients to be back-propagated in an end-to-end manner. Most of the AR models bottleneck training speed when implemented "as is" in the time domain and executed with a parallel processor like GPU due to their infinite impulse response (IIR) filter components. We tackle this by further developing a recently proposed acceleration technique, which borrows the frequency-sampling method (FSM). With the proposed DAR models, we aim to solve an artificial reverberation parameter (ARP) estimation task in a unified approach. We design an ARP estimation network applicable to both analysis-synthesis (RIR-to-ARP) and blind estimation (reverberant-speech-to-ARP) tasks. And using different DAR models only requires slightly a different decoder configuration. This way, the proposed DAR framework overcomes the previous methods' limitations of task-dependency and AR-model-dependency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge