Detection Interval for Diffusion Molecular Communication: How Long is Enough?
Paper and Code
Apr 19, 2022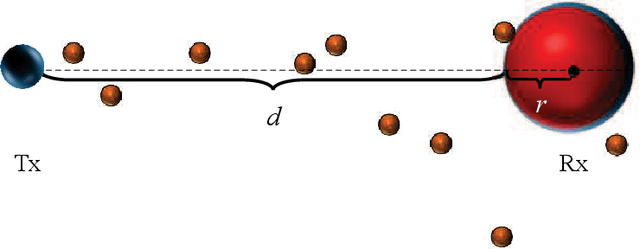
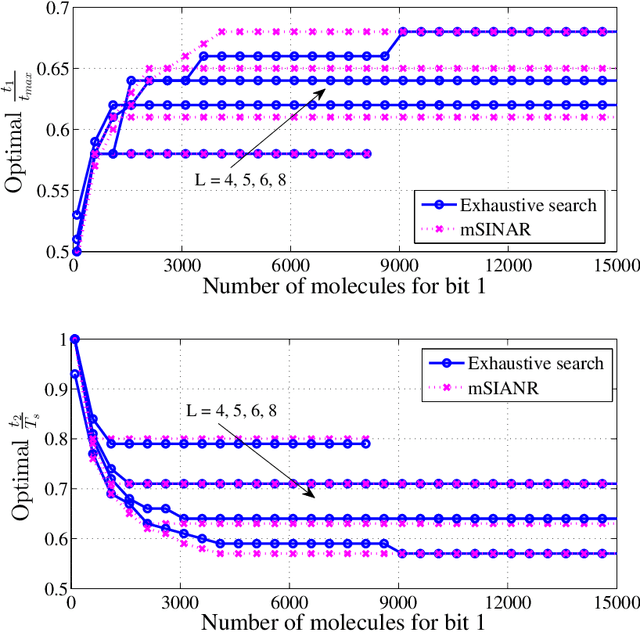
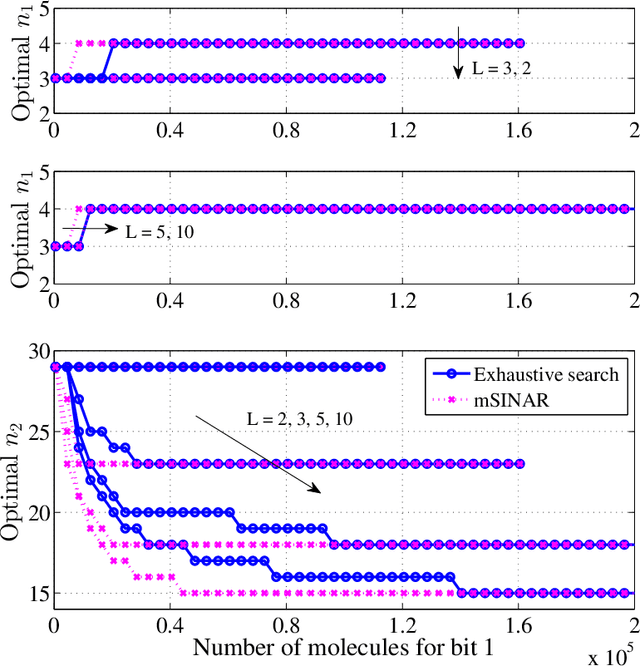
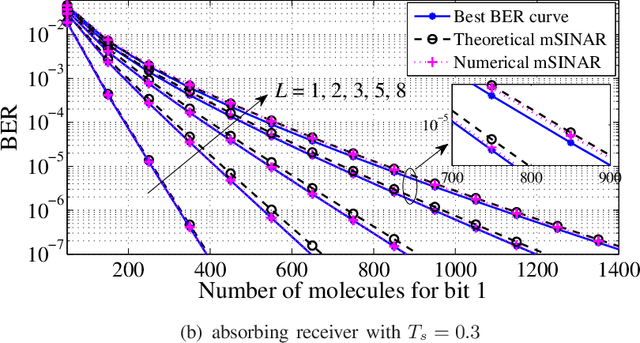
Molecular communication has a key role to play in future medical applications, including detecting, analyzing, and addressing infectious disease outbreaks. Overcoming inter-symbol interference (ISI) is one of the key challenges in the design of molecular communication systems. In this paper, we propose to optimize the detection interval to minimize the impact of ISI while ensuring the accurate detection of the transmitted information symbol, which is suitable for the absorbing and passive receivers. For tractability, based on the signal-to-interference difference (SID) and signal-to-interference-and-noise amplitude ratio (SINAR), we propose a modified-SINAR (mSINAR) to measure the bit error rate (BER) performance for the molecular communication system with a variable detection interval. Besides, we derive the optimal detection interval in closed form. Using simulation results, we show that the BER performance of our proposed mSINAR scheme is superior to the competing schemes, and achieves similar performance to optimal intervals found by the exhaustive search.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge