Detecting dementia in Mandarin Chinese using transfer learning from a parallel corpus
Paper and Code
Mar 03, 2019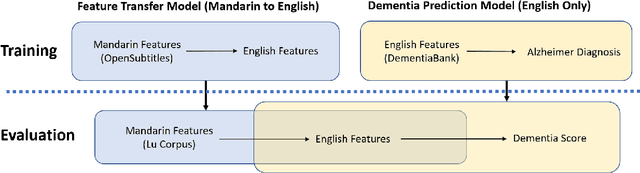
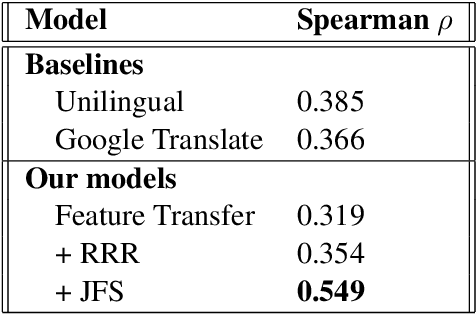
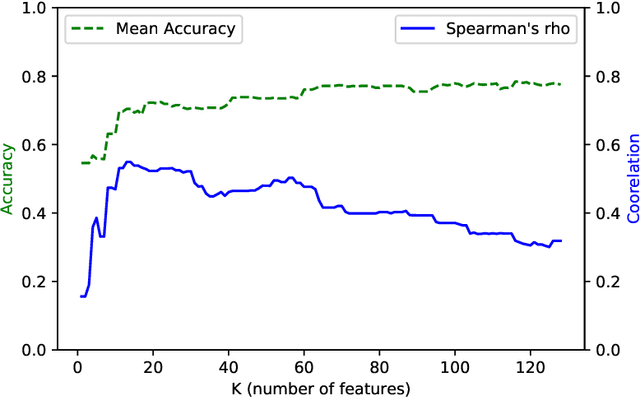
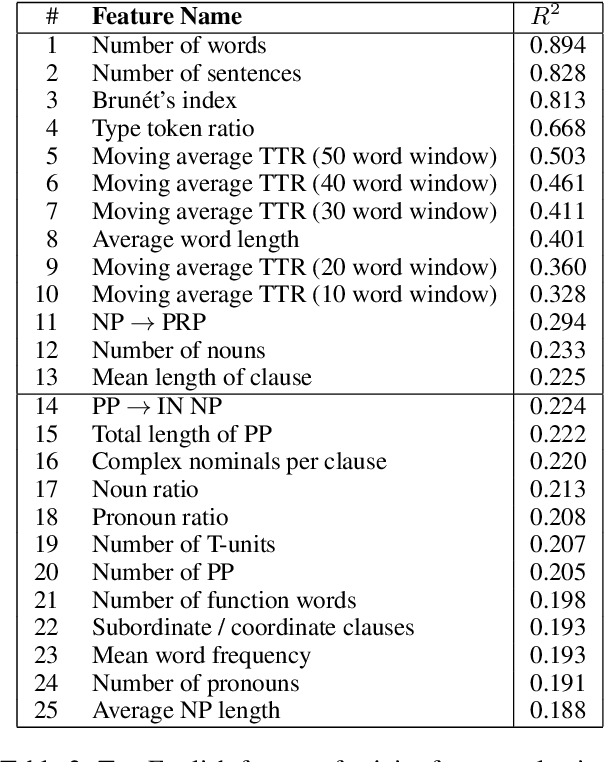
Machine learning has shown promise for automatic detection of Alzheimer's disease (AD) through speech; however, efforts are hampered by a scarcity of data, especially in languages other than English. We propose a method to learn a correspondence between independently engineered lexicosyntactic features in two languages, using a large parallel corpus of out-of-domain movie dialogue data. We apply it to dementia detection in Mandarin Chinese, and demonstrate that our method outperforms both unilingual and machine translation-based baselines. This appears to be the first study that transfers feature domains in detecting cognitive decline.
* NAACL 2019 (Short paper)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge