Describing Images $\textit{Fast and Slow}$: Quantifying and Predicting the Variation in Human Signals during Visuo-Linguistic Processes
Paper and Code
Feb 02, 2024
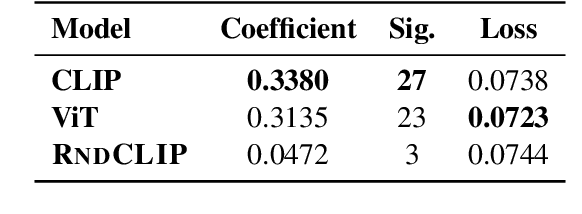

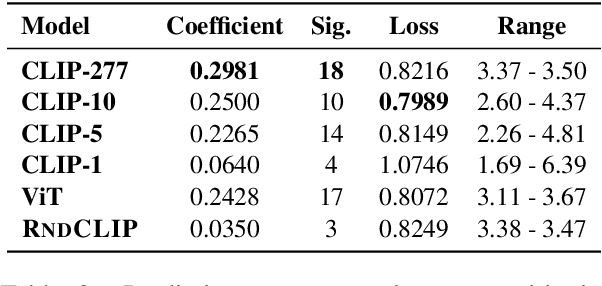
There is an intricate relation between the properties of an image and how humans behave while describing the image. This behavior shows ample variation, as manifested in human signals such as eye movements and when humans start to describe the image. Despite the value of such signals of visuo-linguistic variation, they are virtually disregarded in the training of current pretrained models, which motivates further investigation. Using a corpus of Dutch image descriptions with concurrently collected eye-tracking data, we explore the nature of the variation in visuo-linguistic signals, and find that they correlate with each other. Given this result, we hypothesize that variation stems partly from the properties of the images, and explore whether image representations encoded by pretrained vision encoders can capture such variation. Our results indicate that pretrained models do so to a weak-to-moderate degree, suggesting that the models lack biases about what makes a stimulus complex for humans and what leads to variations in human outputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge