Denoising Fast X-Ray Fluorescence Raster Scans of Paintings
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2022
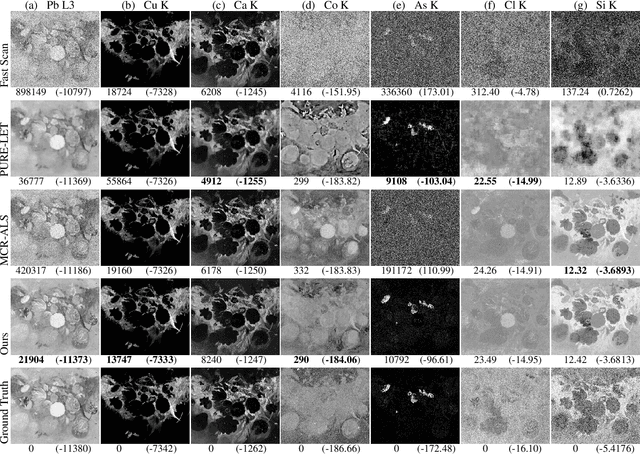

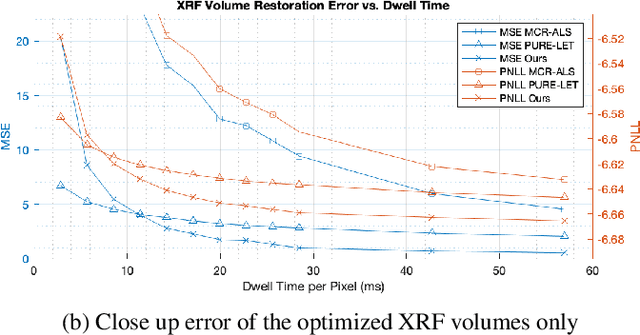
Macro x-ray fluorescence (XRF) imaging of cultural heritage objects, while a popular non-invasive technique for providing elemental distribution maps, is a slow acquisition process in acquiring high signal-to-noise ratio XRF volumes. Typically on the order of tenths of a second per pixel, a raster scanning probe counts the number of photons at different energies emitted by the object under x-ray illumination. In an effort to reduce the scan times without sacrificing elemental map and XRF volume quality, we propose using dictionary learning with a Poisson noise model as well as a color image-based prior to restore noisy, rapidly acquired XRF data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge