Demystifying Inductive Biases for $β$-VAE Based Architectures
Paper and Code
Feb 12, 2021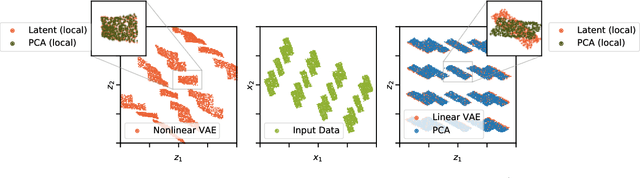
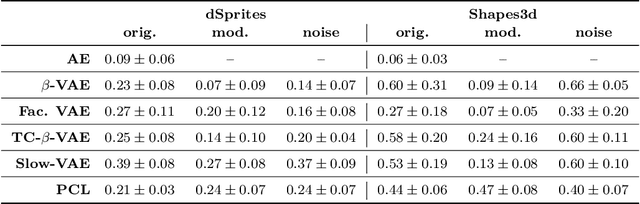
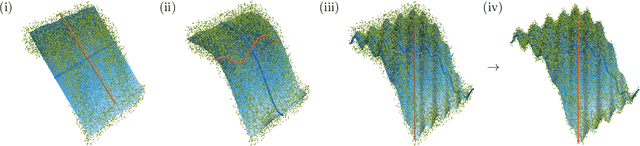
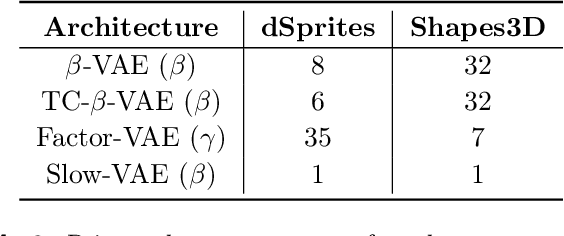
The performance of $\beta$-Variational-Autoencoders ($\beta$-VAEs) and their variants on learning semantically meaningful, disentangled representations is unparalleled. On the other hand, there are theoretical arguments suggesting the impossibility of unsupervised disentanglement. In this work, we shed light on the inductive bias responsible for the success of VAE-based architectures. We show that in classical datasets the structure of variance, induced by the generating factors, is conveniently aligned with the latent directions fostered by the VAE objective. This builds the pivotal bias on which the disentangling abilities of VAEs rely. By small, elaborate perturbations of existing datasets, we hide the convenient correlation structure that is easily exploited by a variety of architectures. To demonstrate this, we construct modified versions of standard datasets in which (i) the generative factors are perfectly preserved; (ii) each image undergoes a mild transformation causing a small change of variance; (iii) the leading \textbf{VAE-based disentanglement architectures fail to produce disentangled representations whilst the performance of a non-variational method remains unchanged}. The construction of our modifications is nontrivial and relies on recent progress on mechanistic understanding of $\beta$-VAEs and their connection to PCA. We strengthen that connection by providing additional insights that are of stand-alone interest.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge