Demonstration of Envariance and Parity Learning on the IBM 16 Qubit Processor
Paper and Code
Feb 07, 2018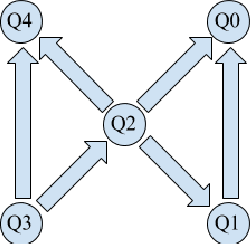

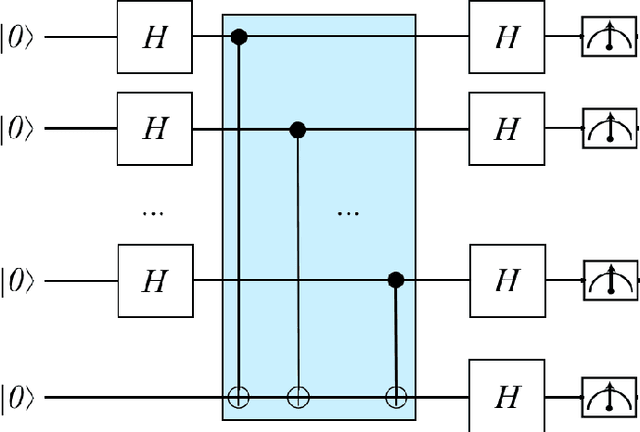
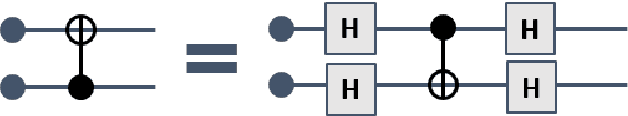
Recently, IBM has made available a quantum computer provided with 16 qubits, denoted as IBM Q16. Previously, only a 5 qubit device, denoted as Q5, was available. Both IBM devices can be used to run quantum programs, by means of a cloud-based platform. In this paper, we illustrate our experience with IBM Q16 in demonstrating entanglement assisted invariance, also known as envariance, and parity learning by querying a uniform quantum example oracle. In particular, we illustrate the non-trivial strategy we have designed for compiling $n$-qubit quantum circuits ($n$ being an input parameter) on any IBM device, taking into account topological constraints.
* 13 pages, 15 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge