Defects Mitigation in Resistive Crossbars for Analog Vector Matrix Multiplication
Paper and Code
Dec 17, 2019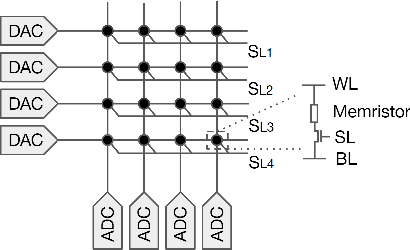
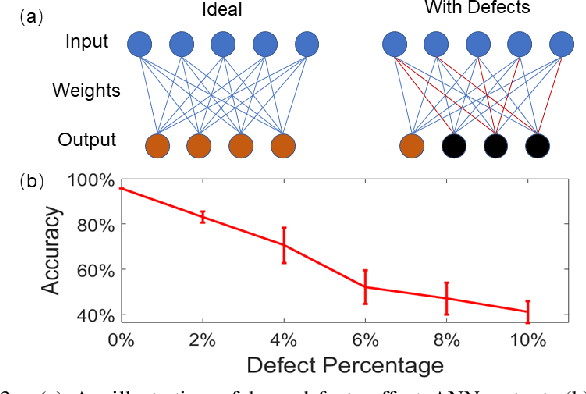
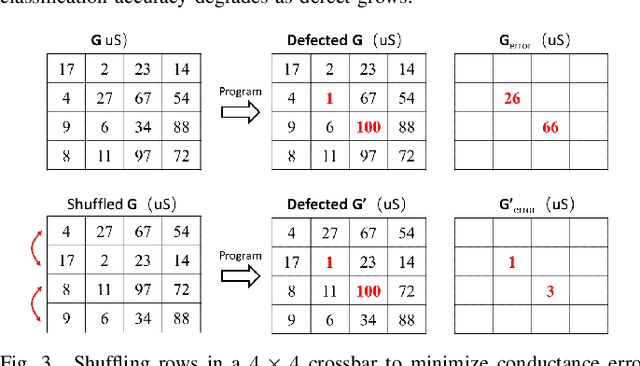
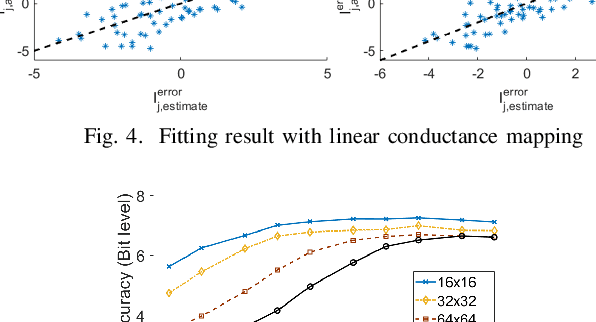
With storage and computation happening at the same place, computing in resistive crossbars minimizes data movement and avoids the memory bottleneck issue. It leads to ultra-high energy efficiency for data-intensive applications. However, defects in crossbars severely affect computing accuracy. Existing solutions, including re-training with defects and redundant designs, but they have limitations in practical implementations. In this work, we introduce row shuffling and output compensation to mitigate defects without re-training or redundant resistive crossbars. We also analyzed the coupling effects of defects and circuit parasitics. Moreover, We study different combinations of methods to achieve the best trade-off between cost and performance. Our proposed methods could rescue up to 10% of defects in ResNet-20 application without performance degradation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge