DeepSeqSLAM: A Trainable CNN+RNN for Joint Global Description and Sequence-based Place Recognition
Paper and Code
Nov 17, 2020
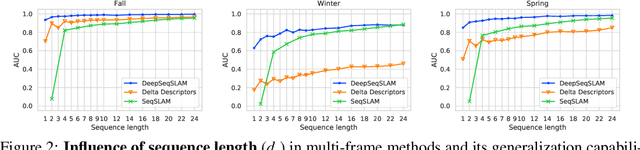


Sequence-based place recognition methods for all-weather navigation are well-known for producing state-of-the-art results under challenging day-night or summer-winter transitions. These systems, however, rely on complex handcrafted heuristics for sequential matching - which are applied on top of a pre-computed pairwise similarity matrix between reference and query image sequences of a single route - to further reduce false-positive rates compared to single-frame retrieval methods. As a result, performing multi-frame place recognition can be extremely slow for deployment on autonomous vehicles or evaluation on large datasets, and fail when using relatively short parameter values such as a sequence length of 2 frames. In this paper, we propose DeepSeqSLAM: a trainable CNN+RNN architecture for jointly learning visual and positional representations from a single monocular image sequence of a route. We demonstrate our approach on two large benchmark datasets, Nordland and Oxford RobotCar - recorded over 728 km and 10 km routes, respectively, each during 1 year with multiple seasons, weather, and lighting conditions. On Nordland, we compare our method to two state-of-the-art sequence-based methods across the entire route under summer-winter changes using a sequence length of 2 and show that our approach can get over 72% AUC compared to 27% AUC for Delta Descriptors and 2% AUC for SeqSLAM; while drastically reducing the deployment time from around 1 hour to 1 minute against both. The framework code and video are available at https://mchancan.github.io/deepseqslam
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge