Deep Slow Motion Video Reconstruction with Hybrid Imaging System
Paper and Code
Feb 27, 2020

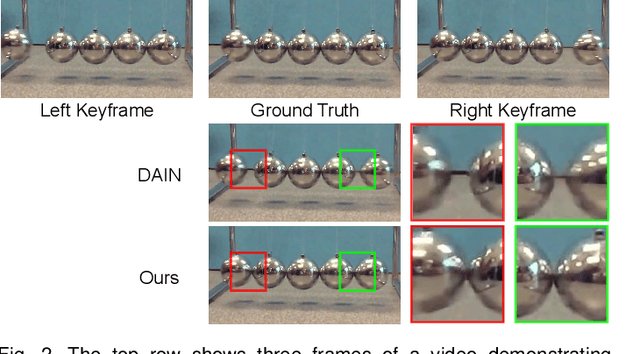

Slow motion videos are becoming increasingly popular, but capturing high-resolution videos at extremely high frame rates requires professional high-speed cameras. To mitigate this problem, current techniques increase the frame rate of standard videos through frame interpolation by assuming linear motion between the existing frames. While this assumption holds true for simple cases with small motion, in challenging cases the motion is usually complex and this assumption is no longer valid. Therefore, they typically produce results with unnatural motion in these challenging cases. In this paper, we address this problem using two video streams as the input; an auxiliary video with high frame rate and low spatial resolution, providing temporal information, in addition to the standard main video with low frame rate and high spatial resolution. We propose a two-stage deep learning system consisting of alignment and appearance estimation that reconstructs high resolution slow motion video from the hybrid video input. For alignment, we propose to use a set of pre-trained and trainable convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to compute the flows between the missing frame and the two existing frames of the main video by utilizing the content of the auxiliary video frames. We then warp the existing frames using the flows to produce a set of aligned frames. For appearance estimation, we propose to combine the aligned and auxiliary frames using a context and occlusion aware CNN. We train our model on a set of synthetically generated hybrid videos and show high-quality results on a wide range of test scenes. We further demonstrate the practicality of our approach by showing the performance of our system on two real dual camera setups with small baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge