Deep-Relative-Trust-Based Diffusion for Decentralized Deep Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 06, 2025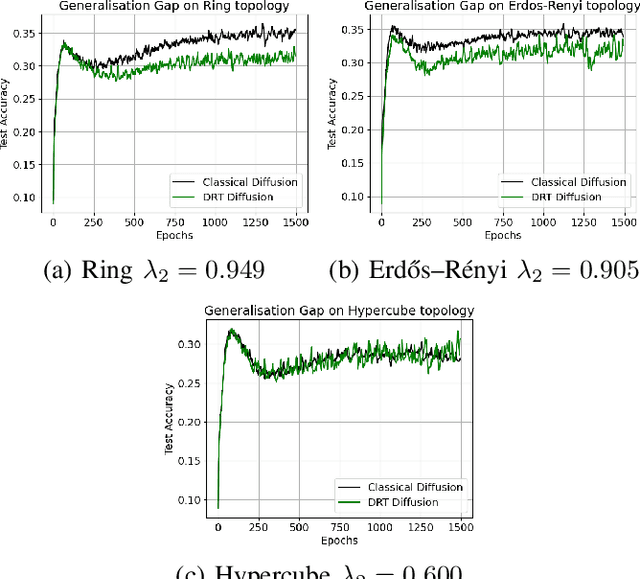
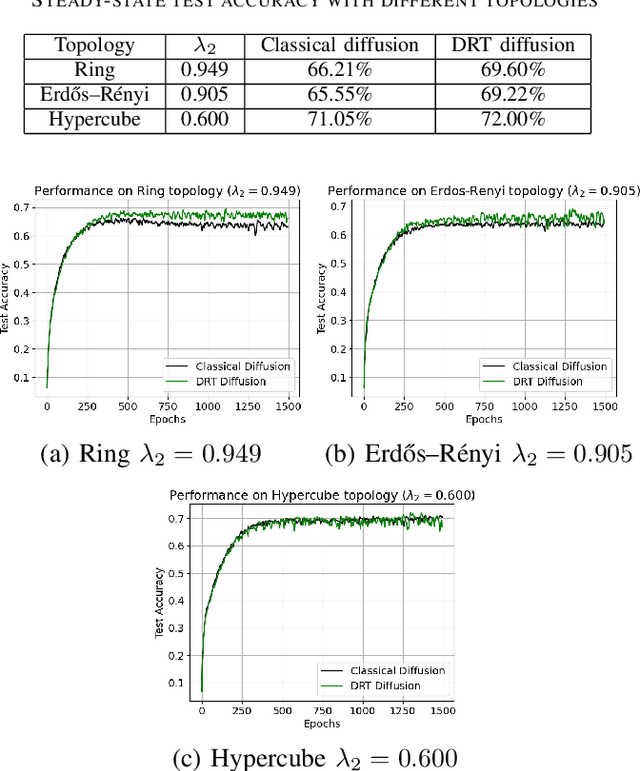
Decentralized learning strategies allow a collection of agents to learn efficiently from local data sets without the need for central aggregation or orchestration. Current decentralized learning paradigms typically rely on an averaging mechanism to encourage agreement in the parameter space. We argue that in the context of deep neural networks, which are often over-parameterized, encouraging consensus of the neural network outputs, as opposed to their parameters can be more appropriate. This motivates the development of a new decentralized learning algorithm, termed DRT diffusion, based on deep relative trust (DRT), a recently introduced similarity measure for neural networks. We provide convergence analysis for the proposed strategy, and numerically establish its benefit to generalization, especially with sparse topologies, in an image classification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge