Deep Metric Learning with Alternating Projections onto Feasible Sets
Paper and Code
Jul 17, 2019
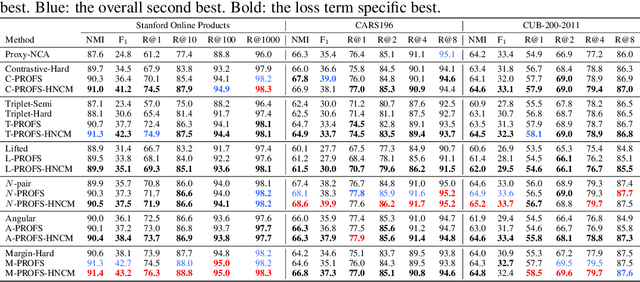
During the training of networks for distance metric learning, minimizers of the typical loss functions can be considered as "feasible points" satisfying a set of constraints imposed by the training data. To this end, we reformulate deep metric learning problem as finding a feasible point of a constraint set where the embedding vectors of the training data satisfy desired intra-class and inter-class proximity. The feasible set induced by the constraint set is expressed as the intersection of the relaxed feasible sets which enforce the proximity constraints only for particular samples (a sample from each class) of the training data. Then, the feasible point problem is to be approximately solved by performing alternating projections onto those feasible sets. Such an approach results in minimizing a typical loss function with a systematic batch set construction where these batches are constrained to contain the same sample from each class for a certain number of iterations. Moreover, these particular samples can be considered as the class representatives, allowing efficient utilization of hard class mining during batch construction. The proposed technique is applied with the contrastive, triplet, lifted structured, $N$-pair, angular and margin-based losses and evaluated on Stanford Online Products, CAR196 and CUB200-2011 datasets for image retrieval and clustering. The proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art for all 6 loss functions with no additional computational cost and boosts its performance further by hard negative class mining.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge