Deep Learning with a Classifier System: Initial Results
Paper and Code
Mar 01, 2021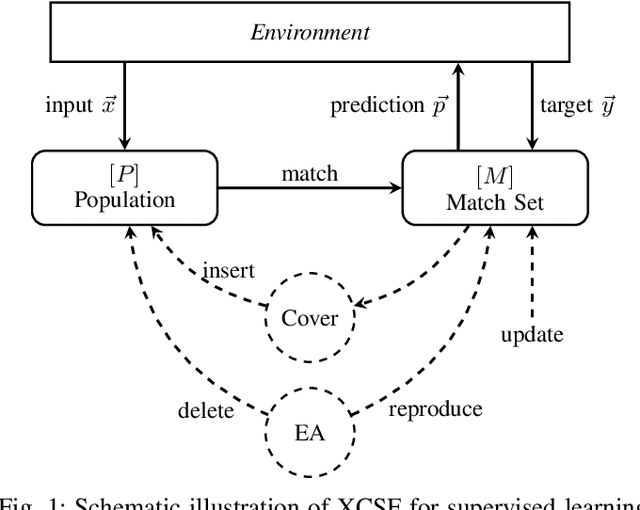


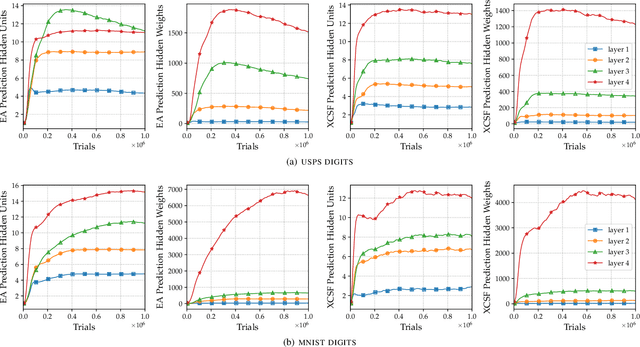
This article presents the first results from using a learning classifier system capable of performing adaptive computation with deep neural networks. Individual classifiers within the population are composed of two neural networks. The first acts as a gating or guarding component, which enables the conditional computation of an associated deep neural network on a per instance basis. Self-adaptive mutation is applied upon reproduction and prediction networks are refined with stochastic gradient descent during lifetime learning. The use of fully-connected and convolutional layers are evaluated on handwritten digit recognition tasks where evolution adapts (i) the gradient descent learning rate applied to each layer (ii) the number of units within each layer, i.e., the number of fully-connected neurons and the number of convolutional kernel filters (iii) the connectivity of each layer, i.e., whether each weight is active (iv) the weight magnitudes, enabling escape from local optima. The system automatically reduces the number of weights and units while maintaining performance after achieving a maximum prediction error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge