Deep Learning-based Codes for Wiretap Fading Channels
Paper and Code
Sep 13, 2024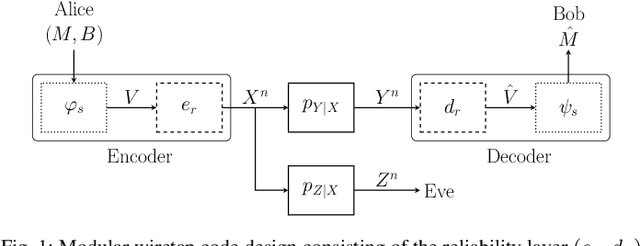



The wiretap channel is a well-studied problem in the physical layer security (PLS) literature. Although it is proven that the decoding error probability and information leakage can be made arbitrarily small in the asymptotic regime, further research on finite-blocklength codes is required on the path towards practical, secure communications systems. This work provides the first experimental characterization of a deep learning-based, finite-blocklength code construction for multi-tap fading wiretap channels without channel state information (CSI). In addition to the evaluation of the average probability of error and information leakage, we illustrate the influence of (i) the number of fading taps, (ii) differing variances of the fading coefficients and (iii) the seed selection for the hash function-based security layer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge