Deep Feature Learning from a Hospital-Scale Chest X-ray Dataset with Application to TB Detection on a Small-Scale Dataset
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2019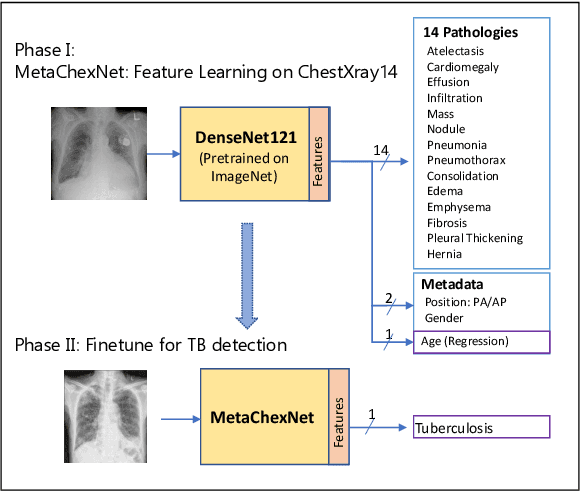
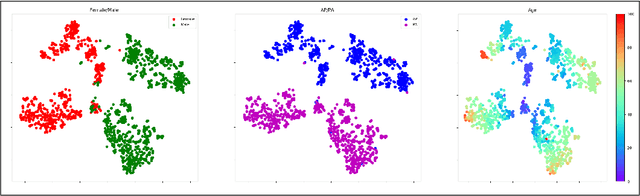
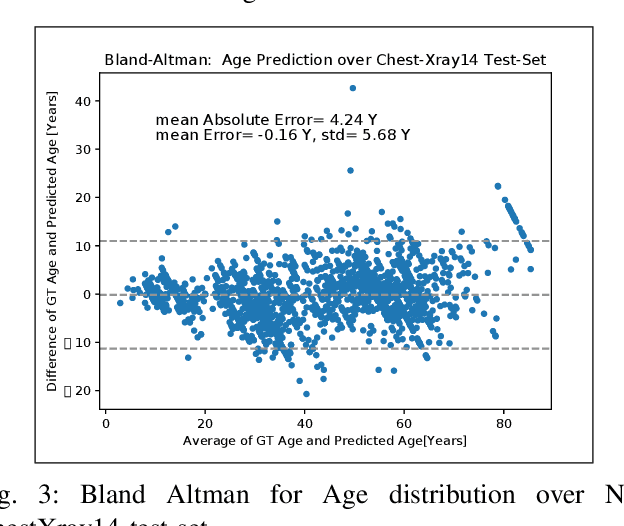
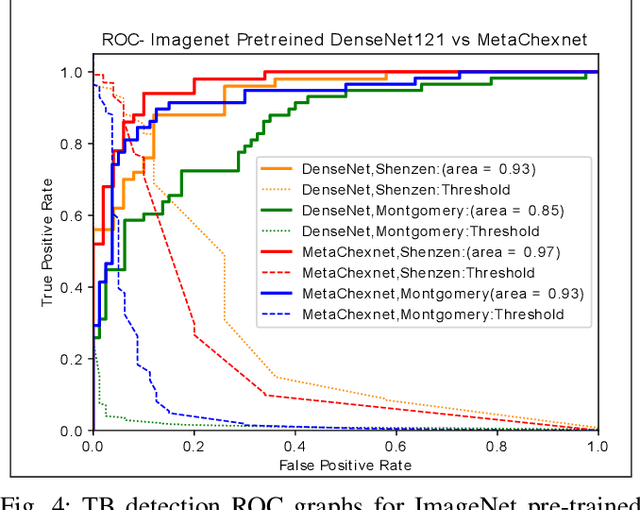
The use of ImageNet pre-trained networks is becoming widespread in the medical imaging community. It enables training on small datasets, commonly available in medical imaging tasks. The recent emergence of a large Chest X-ray dataset opened the possibility for learning features that are specific to the X-ray analysis task. In this work, we demonstrate that the features learned allow for better classification results for the problem of Tuberculosis detection and enable generalization to an unseen dataset. To accomplish the task of feature learning, we train a DenseNet-121 CNN on 112K images from the ChestXray14 dataset which includes labels of 14 common thoracic pathologies. In addition to the pathology labels, we incorporate metadata which is available in the dataset: Patient Positioning, Gender and Patient Age. We term this architecture MetaChexNet. As a by-product of the feature learning, we demonstrate state of the art performance on the task of patient Age \& Gender estimation using CNN's. Finally, we show the features learned using ChestXray14 allow for better transfer learning on small-scale datasets for Tuberculosis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge