Deep Convolutional Neural Network Applied to Electroencephalography: Raw Data vs Spectral Features
Paper and Code
May 11, 2021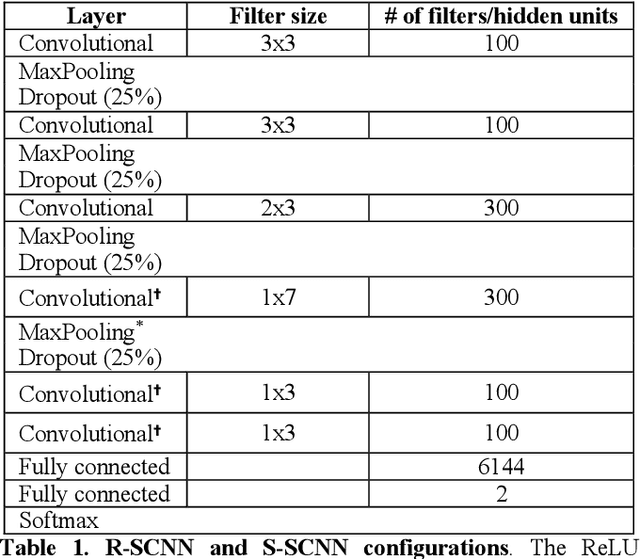

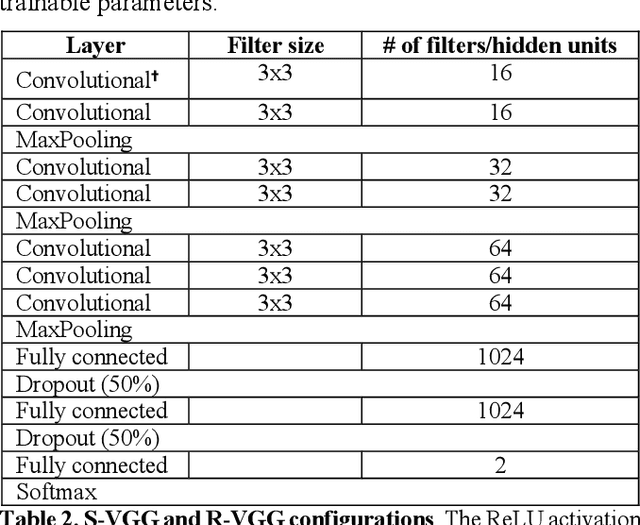
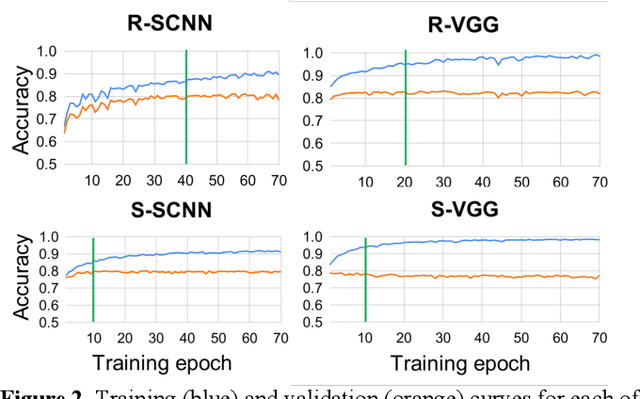
The success of deep learning in computer vision has inspired the scientific community to explore new analysis methods. Within the field of neuroscience, specifically in electrophysiological neuroimaging, researchers are starting to explore leveraging deep learning to make predictions on their data without extensive feature engineering. This paper compares deep learning using minimally processed EEG raw data versus deep learning using EEG spectral features using two different deep convolutional neural architectures. One of them from Putten et al. (2018) is tailored to process raw data; the other was derived from the VGG16 vision network (Simonyan and Zisserman, 2015) which is designed to process EEG spectral features. We apply them to classify sex on 24-channel EEG from a large corpus of 1,574 participants. Not only do we improve on state-of-the-art classification performance for this type of classification problem, but we also show that in all cases, raw data classification leads to superior performance as compared to spectral EEG features. Interestingly we show that the neural network tailored to process EEG spectral features has increased performance when applied to raw data classification. Our approach suggests that the same convolutional networks used to process EEG spectral features yield superior performance when applied to EEG raw data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge