Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoders with Aggregated Multi-Resolution Skip Connections for Skin Lesion Segmentation
Paper and Code
Jan 26, 2019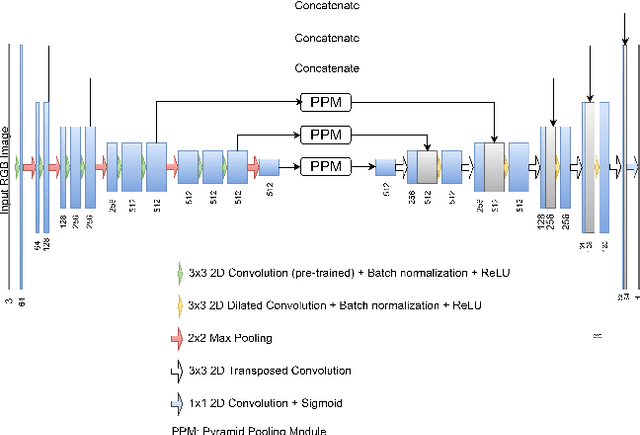
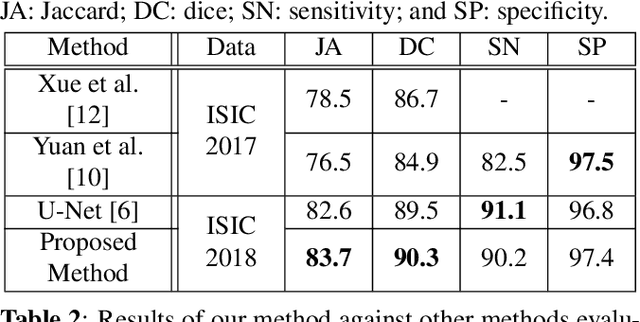
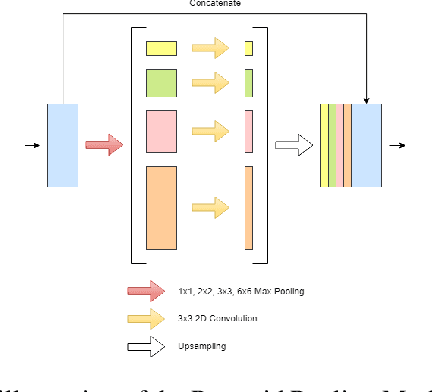
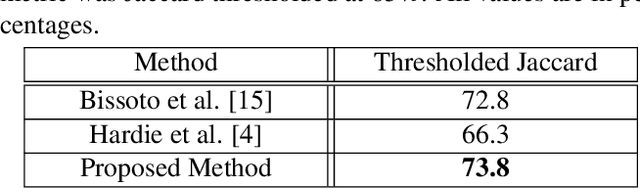
The prevalence of skin melanoma is rapidly increasing as well as the recorded death cases of its patients. Automatic image segmentation tools play an important role in providing standardized computer-assisted analysis for skin melanoma patients. Current state-of-the-art segmentation methods are based on fully convolutional neural networks, which utilize an encoder-decoder approach. However, these methods produce coarse segmentation masks due to the loss of location information during the encoding layers. Inspired by Pyramid Scene Parsing Network (PSP-Net), we propose an encoder-decoder model that utilizes pyramid pooling modules in the deep skip connections which aggregate the global context and compensate for the lost spatial information. We trained and validated our approach using ISIC 2018: Skin Lesion Analysis Towards Melanoma Detection grand challenge dataset. Our approach showed a validation accuracy with a Jaccard index of 0.837, which outperforms U-Net. We believe that with this reported reliable accuracy, this method can be introduced for clinical practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge